Fig. 2.
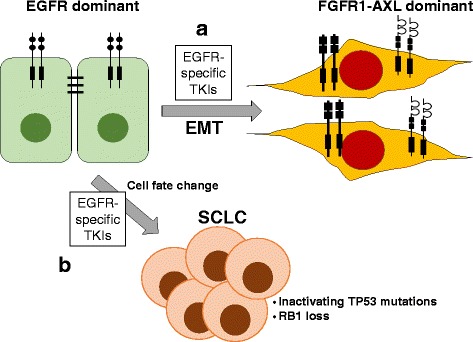
Phenotypic changes in EGFR mutant LUAD as a mechanism of resistance to targeted therapy. a In response to EGFR inhibitors, multiple groups have observed that EGFR mutant LUAD can undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cells that have undergone EMT no longer rely on oncogenic EGFR as a driver, but rather on FGF2-FGFR1 and AXL signaling pathways induced as a consequence of EMT. b Clinically, EGFR mutant LUADs treated with EGFR-specific TKIs undergo a phenotypic switch to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accompanied by TP53 mutant and loss of RB1 expression. This cell fate change has not been observed with in vitro models and the kinetics and mechanism are not well understood
