Fig. 6. Schematic representation of the effect of the DnaK system on the one-dimensional projection of the folding free-energy landscape under force and its associated folding kinetics.
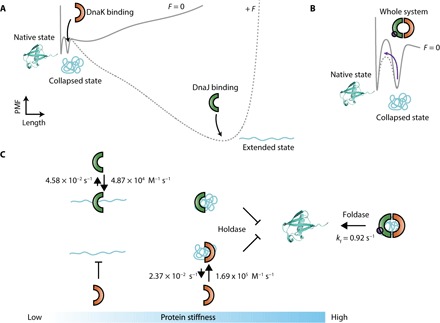
(A) One-dimensional representation of the force modulation of the ubiquitin free-energy landscape, highlighting the different conformations (native, collapsed, and extended) (31). While DnaJ binds the unfolded and extended state, preventing protein refolding, DnaK stabilizes the collapsed conformations instead. (B) By contrast, the whole DnaKJE complex catalyzes the collapsed–to–native state transition. (C) Kinetic scheme highlighting the dynamic interaction—hallmarked by the related binding (kon) and dissociation constants (koff)—between each chaperone and the distinct conformation of the ubiquitin substrate (at a force of 170 pN for the extended conformation). The protein-chaperone interaction has direct implications for protein elasticity.
