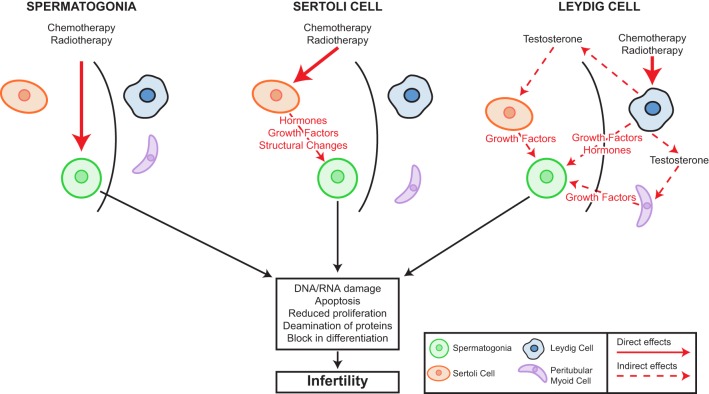
Figure 2.
Cellular targets for chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy-induced damage in the prepubertal testis. Infertility may result from damage within the seminiferous tubules as a result of direct damage to the spermatogonia leading to alterations in proliferation, differentiation, protein deamination and apoptosis and ultimately infertility. Alternatively, damage to the Sertoli cells by such treatments may result in alterations in hormones, growth factors or seminiferous tubule structure that will indirectly mediate the effects of chemo/radiotherapy on the germ cells. Similarly, interstitial effects include damage to the Leydig cells that can lead to alterations in hormones or growth factors that may impact germ cells directly or indirectly (e.g. testosterone deficiency) through effects other somatic cell populations.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a