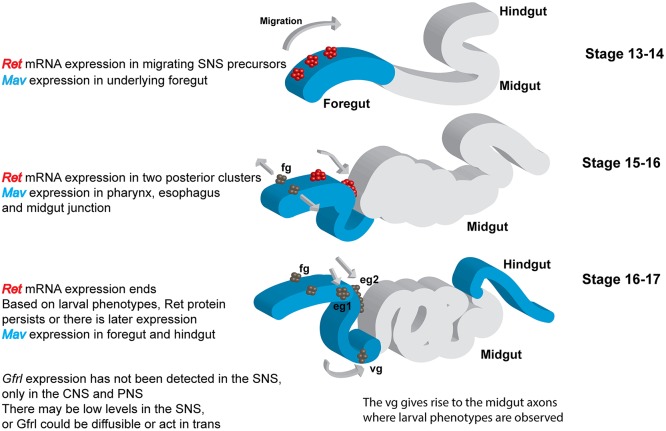
Fig. 8.
Summary of Ret and mav expression during development of the stomatogastric nervous system. Ret exhibits highly dynamic mRNA expression in the embryo (Hahn and Bishop, 2001; Hernández et al., 2015). Ret is also expressed in adult midgut precursors at an earlier stage in development, as well as in discrete cells in the CNS, PNS and Malpighian tubules (not shown). mav mRNA is expressed weakly in the foregut primordium and at later stages in the pharynx, esophagus and proventriculus (Nguyen et al., 2000). Our analysis of an epitope-tagged Mav expressed at endogenous levels indicates strong expression in the epithelial region from which the SNS precursor clusters delaminate (Fig. 6E) and expansion to match the pattern of the mRNA, becoming concentrated near the sites at which the SNS neurons stop migrating (junction of the pharynx and esophagus, proventriculus; Fig. 6F,G). mav is also expressed in the epidermis and visceral mesoderm. Apart from promoter fragments driving reporters, Gfrl expression has not been observed in the SNS (Kallijärvi et al., 2012). Gfrl could therefore be expressed at low levels, or the protein might be acting in trans or in a soluble form (Paratcha et al., 2001). Gfrl promoter fragments continue to drive expression in the anterior midgut of the larvae (Hernández et al., 2015). eg1 and eg2, esophageal ganglia; fg, frontal ganglion; vg, ventricular ganglion.