Fig. 1.
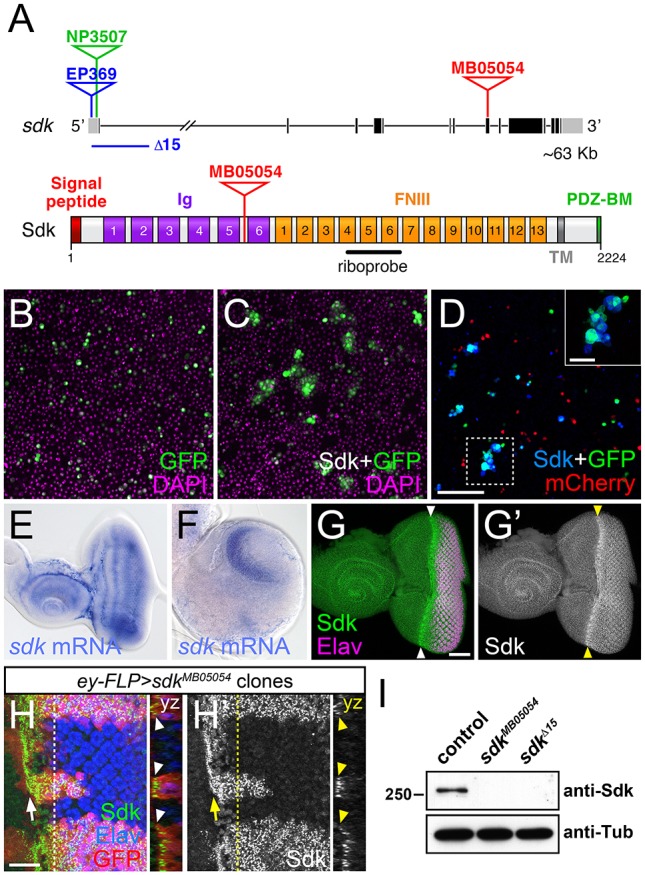
Sdk is a homophilic adhesion molecule expressed in the visual system. (A) The sdk gene (top) with coding exons in black and non-coding exons in gray, showing the positions of the MB05054 Minos insertion, the EP369 P element insertion and derived Δ15 deletion, and the NP3507 GAL4 insertion. The Sdk protein (bottom) has six Ig domains, 13 FNIII domains, a transmembrane domain (TM) and a PDZ-binding motif (PDZ-BM). (B-D) Aggregates formed by S2 cells transfected with Actin5c (Act)-GAL4 and UAS-GFP (green) (B); Act-GAL4, UAS-HA-Sdk and UAS-GFP (C); and a mixture of cells transfected with Act-GAL4, UAS-HA-Sdk and UAS-GFP, and with Act-GAL4 and UAS-mCherry (red) (D). DAPI is in magenta (B,C) and anti-HA in blue (D). Inset provides an enlargement of the boxed region. Sdk-expressing cells form aggregates that lack cells not transfected with Sdk. (E,F) In situ hybridization with a sdk probe on a third-instar eye-antennal imaginal disc (E) and brain (F). sdk is expressed throughout the eye disc and enriched in the optic lobes of the brain. Posterior is towards the right in E-H′. (G) Anti-Sdk (G′, green in G) and anti-Elav (magenta) labeling of an eye-antennal disc, showing enrichment of Sdk protein posterior to the morphogenetic furrow (arrowheads). (H) Anti-Sdk (H′, green in H) and anti-Elav (blue) labeling of an eye disc containing sdkMB05054 mutant clones marked by the absence of GFP (red). Sdk labeling is absent from the clones. An arrow indicates the morphogenetic furrow. yz sections show Sdk accumulation at the apical surface of the disc (arrowheads). (I) Western blot of extracts from w1118 (control), sdkMB05054 and sdkΔ15 embryos, probed with anti-Sdk and anti-Tubulin (Tub). Sdk protein is not detected in either mutant. Scale bars: 100 µm in D; 30 µm in G and inset in D; 10 µm in H,H′.
