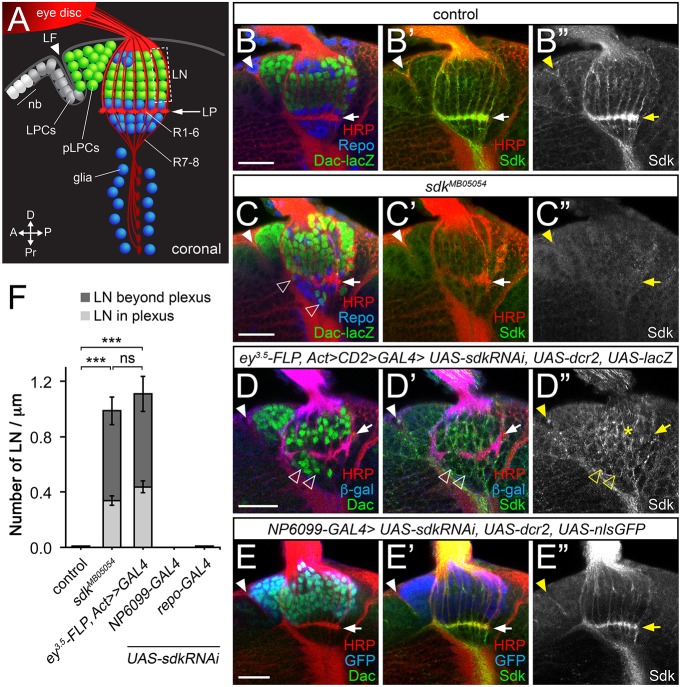
Fig. 2.
Lamina neuron placement requires sdk in photoreceptors. (A) Diagram of a coronal section through the third-instar larval brain, showing neuroblasts (nb) and lamina precursor cells (LPCs), which become postmitotic (pLPCs) behind the lamina furrow (LF; arrowhead) and differentiate into lamina neurons (LN) aligned into columns along the axons of R1-R6. Glia are shown in blue. (B-E″) Confocal images of the same view of larval brains for: (B-B″) control (sdkMB05054/+); (C-C″) sdkMB05054; (D-D″) sdk knockdown in the eye with ey3.5-FLP, Act>CD2>GAL4 [Sdk still accumulates in LNs (asterisk)]; and (E-E″) sdk knockdown in the lamina with NP6099-GAL4. A-E″ are labeled with anti-Sdk (B″,C″,D″,E″, green in B′,C′,D′,E′), anti-HRP to mark photoreceptor axons (red in B,B′,C,C′,D,D′,E,E′), anti-β-galactosidase (β-gal) reflecting dac-lacZ (green in B,C) or anti-Dac (green in D,E) to mark lamina neurons, anti-Repo to mark glia (blue in B,C), or anti-β-gal (blue in D,D′) or anti-GFP (blue in E,E′) to mark the domain of RNAi expression. Lamina neurons are misplaced in sdk mutants and when sdk is knocked down in the eye (empty arrowheads, C,D), but not when it is knocked down in lamina neurons or in glia with repo-GAL4. Filled arrowheads mark the lamina furrow. (F) The number of LNs per µm in or beyond the lamina plexus (LP; arrows in A-E′) in the indicated genotypes. Data are mean±s.e.m. n=15 (sdkΔ7, a precise excision of sdkMB05054 used as a control, and sdkMB05054), n=10 (ey3.5-FLP, Act>CD2>GAL4; sdk RNAi; UAS-dcr2), n=18 (NP6099>sdk RNAi; UAS-dcr2) and n=14 (repo>sdk RNAi; UAS-dcr2). ***P<0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test; ns, not significant. Scale bars: 20 µm.