Fig. 11.
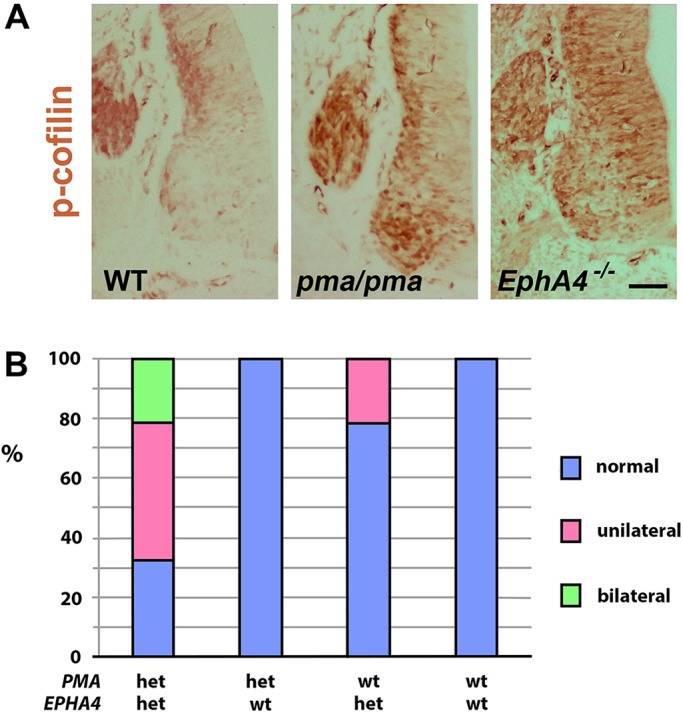
Interaction between pma and Epha4 mutations. (A) P-cofilin immunohistochemistry (brown) on transverse sections of neural tube of E11.5 wild-type (WT), pma/pma and Epha4−/− mouse embryos. Compared with wild type, p-cofilin is at higher levels in both pma/pma and Epha4 mutant mice, suggesting a shared biochemical pathway. Similar levels of protein in the dorsal root ganglia provide an internal control for staining. (B) Representation of frequency occurrence of peroneal nerve loss in postnatal day 21 mice that are compound heterozygotes for EphA4 and pma, compared with single heterozygous littermates for either gene, or littermates wild-type at both loci. See main text for details. Scale bar: 35 µm.
