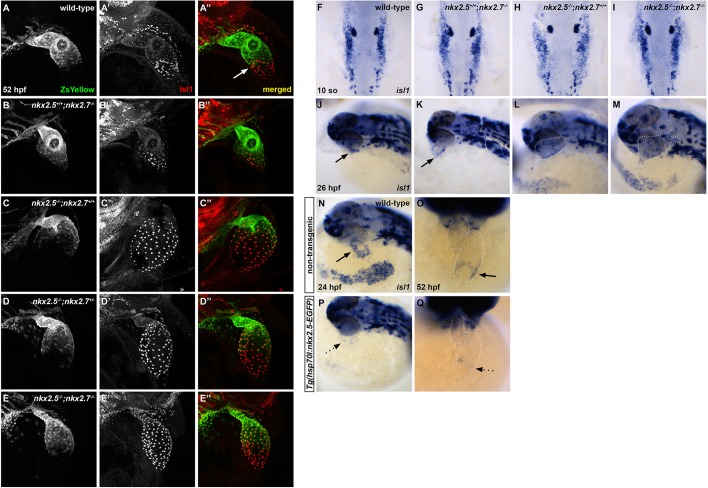
Fig. 5.
Nkx2.5 is not required for isl1+ progenitor specification, but is sufficient to repress isl1 at the venous pole. (A-E″) Representative confocal images, lateral view, anterior towards the top, at 52 hpf. Immunostaining for Isl1 (red) in embryos carrying Tg(nkx2.5:ZsYellow) demonstrates that Isl1 is restricted to the venous pole and Nkx2.5 expression is absent in this region in wild-type (white arrow) (A-A″) and nkx2.5+/+;nkx2.7−/− (B-B″) embryos. However, Isl1 expression is derepressed in the atrium of nkx2.5−/−;nkx2.7+/+ (C-C″) and nkx2.5−/−;nkx2.7+/− (D-D″) embryos, and expands towards the outflow tract in nkx2.5−/−;nkx2.7−/− (E-E″) embryos. (F-I) Dorsal view, anterior towards the top, at 10 somites. In situ hybridization shows no variation in ALPM isl1 expression between wild-type (F) and nkx mutant (G-I) embryos. (J-M) Lateral view, anterior towards the left, at 26 hpf. In situ hybridization demonstrates that isl1 expression is restricted to a ring at the venous pole of the heart tube in wild-type (J) and nkx2.5+/+;nkx2.7−/− (K) embryos. However, isl1 expression expands to the atrium in nkx2.5−/−;nkx2.7+/+ embryos (L) and throughout the entire heart tube in nkx2.5−/−;nkx2.7−/− embryos (M). Black arrows indicate the ring of isl1 expression near the IFT (J,K). (N-Q) Lateral view, anterior towards the left, at 24 hpf (N,P) and ventral view, anterior towards the top, at 52 hpf (O,Q) in non-transgenic (N,O) and Tg(hsp70l:nkx2.5-EGFP) (P,Q) embryos. In situ hybridization demonstrates that isl1 expression is restricted to a ring at the venous pole (black arrows) at 24 hpf (n=9) (N) and 52 hpf (n=7) (O), and that overexpression of nkx2.5 inhibits isl1 expression specifically in this region (dotted arrows) at 24 hpf (n=9/11) (P) and 52 hpf (n=8/9) (Q).