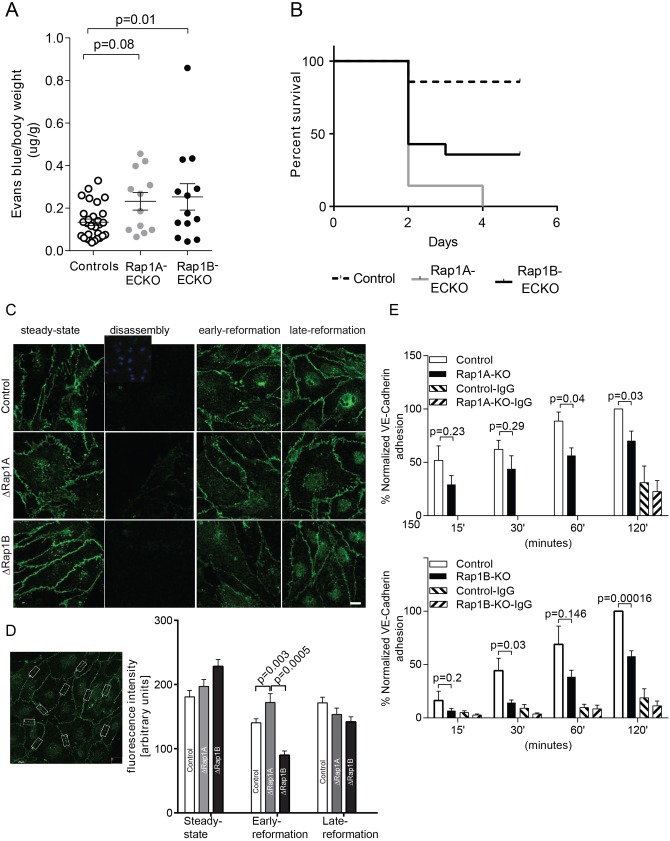
Fig. 3.
Both Rap1 isoforms are required for junction reformation. (A,B) Increased vascular permeability and mortality in Rap1A-ECKO and Rap1B-ECKO mice under LPS-induced inflammatory conditions. (A) Increased vascular permeability to Evans Blue-labeled BSA in Rap1A-ECKO and Rap1B-ECKO mice 5 h after retro-orbital injection of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from Escherichia coli 055:B5 (30 mg/kg). Evans Blue dye concentration was determined as in Fig. 1. Shown are average values, normalized, as indicated; error bars are s.e.m. (n≥12). (B) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice following 30 mg/kg LPS IP injection (n=14). (C,D) Both Rap1 isoforms, and in particular Rap1B, are required for de novo AJ formation. (C) Delayed VE-cadherin fluorescence recovery in AJs of Rap1-deficient ECs following AJ disruption by Ca2+ switch. Confluent MLECs (‘steady state’) were treated with 4 mM EGTA for 15 min at 37°C to disrupt endothelial cell–cell contacts (‘disassembly’). MLECs were allowed to reform AJs by further incubation in 1.8 mM Ca2+-containing culture medium for 2 h (‘early re-formation’) and 6 h (‘late re-formation’). Representative confocal images are shown. Insert in the top row shows DAPI nuclear staining. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) The intensity of VE-cadherin fluorescence in AJs was quantified in 10 boxed areas/view/experimental condition, as shown in the example image on the left. Graph indicates significantly decreased fluorescence intensity in early AJ in Rap1-deficient MLECs (n=3; error bars are s.e.m.). (E) Rap1 deletion leads to attenuated VE-cadherin homophilic binding. Time course of adhesion of calcein-AM-loaded ECs onto Fc-VE-cadherin-coated plates protein as a measure of the ability of ECs to form AJs. Fc-IgG-coated wells serve as negative controls (error bars are s.e.m.; n≥3).