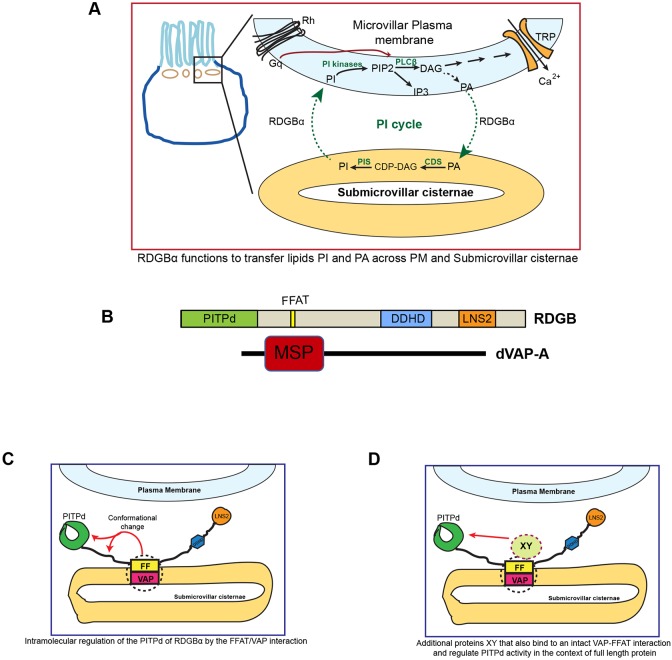
Fig. 8.
RDGBα function at the PM–ER membrane contact site. (A) Schematic representation of the PIP2 cycle, which runs between the plasma membrane and the underlying sub-microvillar cisternae (SMC) in photoreceptors. RDGBα transfers the lipid PI from SMC to PM and transfers PA back from PM to SMC. CDS, CDP diacylglycerol synthase; CDP, cytidine diphosphate; DAG, diacylglcerol; PIS, PI synthase; TRP, transient receptor potential channel. (B) Representation (drawn to scale) of various domains and motifs in RDGBα and dVAP-A. (C) Hypothesized topology of RDGBα and VAP depicting the binding of its FFAT motif to VAP on the SMC. The FFAT–VAP interaction results in an intramolecular conformational change which is important for activity of the PITP domain. (D) Alternative molecular mechanism for the ability of the FFAT–VAP interaction to regulate the function of the PITP domain. The FFAT–VAP interaction recruits and activates a presently undefined effector ‘XY’ which is able to regulate the activity of PITP domain.