Figure 4.
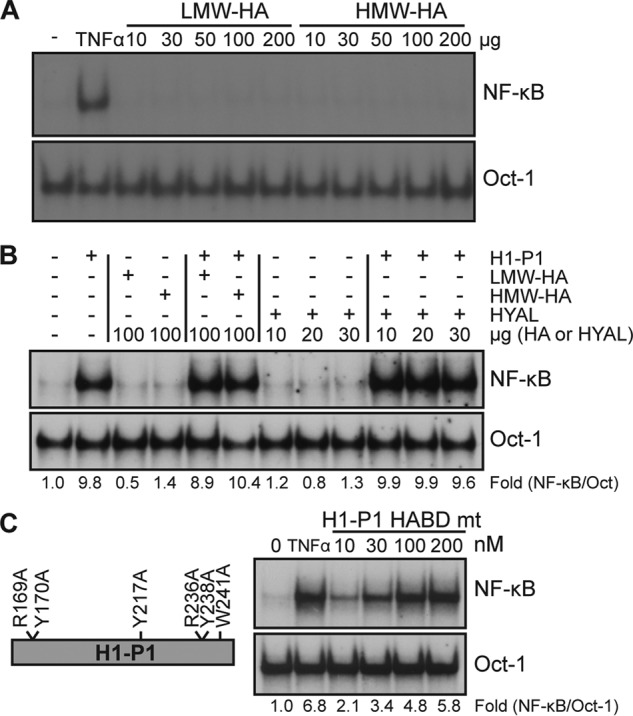
Hyaluronic acid binding is unnecessary for HAPLN1-PTR1–induced NF-κB activation. A, EMSA analysis of NF-κB activity in RPMI8226 cells following incubation with low-molecular weight HA (LMW-HA; 29 kDa) or high molecular weight HA (HMW-HA; 289 kDa) at the microgram amounts indicated for 2 h. Results are representative of two independent experiments. B, EMSA analysis of RPMI8226 cells treated with 100 nm H1-P1, low-molecular weight HA, high-molecular weight HA, or hyaluronidase (HYAL) in the amounts indicated for 4 h. C, H1-P1 HA-binding mutant (H1-P1 HABD mt) was made by mutating the critical residues necessary for HA binding within H1-P1 to alanine where illustrated. RPMI8226 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations (nm) of recombinant GST-fused H1-P1 HABD mt for 4 h and assayed by EMSA. Results are representative of three independent experiments. -Fold change of NF-κB activity was determined as described previously.
