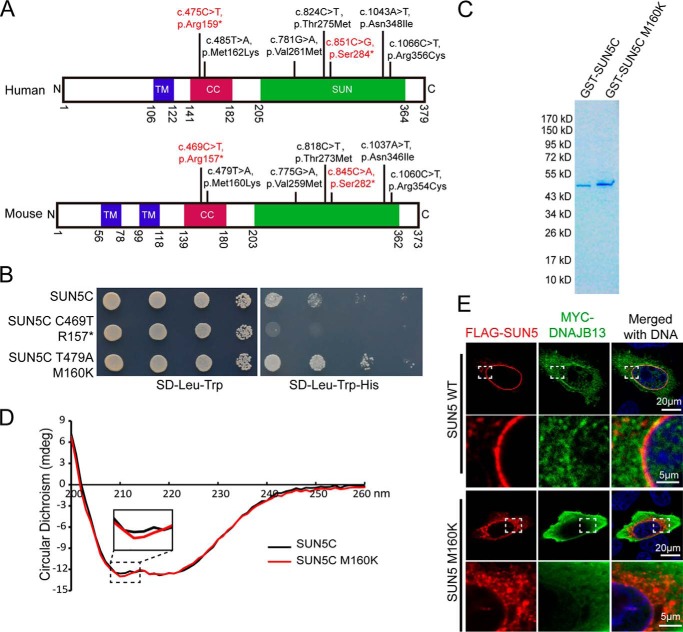
Figure 5.
The secondary structure of the SUN5 protein was altered by mutations in the coiled-coil domain. A, the mutations in the coiled-coil domain and the SUN domain were observed in human and mouse SUN5, showing that these mutations are highly conserved. Due to codon degeneracy, human Ser-284 is coded by TCA, whereas mouse Ser-282 is coded by TCG. Consistent with the human non-sense mutation, 851C→G (TCA-TGA), the corresponding nucleotide (845C) in mouse was mutated to A (TCG-TAG). Other mutations in mouse were consistent with those found in human. B, influence of two mutations in the coiled-coil domain on the SUN5–DNAJB13 interaction as revealed by the Y2H assay. WT SUN5C or its variants were co-transformed with DNAJB13 in the Y2H assay, and yeast cells were diluted by 101, 102, and 103. Aliquots were spotted onto control (SD-Leu-Trp) and selective (SD-Leu-Trp-His) plates. C, protein purification of GST–SUN5C and its variant. The samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. D, the secondary structure of SUN5C was altered by M160K as revealed by CD analysis. E, the NE localization of full-length SUN5 in HeLa cells was impaired by the M160K mutation. WT–FLAG–SUN5 or FLAG–SUN5 M160K, together with MYC–DNAJB13, were co-transfected into HeLa cells. After a 24-h incubation, the transfected cells were immunostained with mouse anti-FLAG (red) and rabbit anti-MYC (green) antibodies. The nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). WT–FLAG–SUN5 localized to the NE, and DNAJB13 was partially recruited to the NE (upper panels), whereas FLAG–SUN5 M160K showed abnormal localization and could not recruit DNAJB13 to the NE (lower panels). The boxed areas have been enlarged in the lower row.