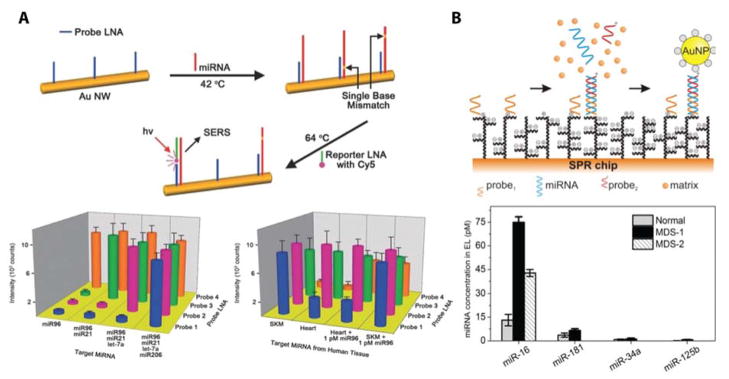
Figure 7.
Successful multiplexing strategies using plasmonic based biosensors. (A) Plasmonic nanowires detected the presence of four miRNA targets using locked nucleic acid capture probes and Cy5 functionalized reporter locked nucleic acid sequences. These optimized nanosensors were used to profile the expression of four miRNAs from RNA isolated from two tissue types. Reproduced from Ultra-Specific Zeptmole microRNA Detection by Plasmonic Nanowire Interstice Sensor with Bi-Temperature Hybridization, Kang, T.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. M.; Lee, H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kang, G.; Seo, M.-K.; Chung, B. H.; Jung, Y.; Kim, B. Small, Vol. 10, Issue 20 (ref 91). Copyright 2014 Wiley. (B) A novel ultra-low fouling surface plasmon resonance imaging biosensor detected four miRNAs from erythrocyte lysate. A gold nanoparticle signal enhancement strategy was used to improve limits of detection. Clinical utility was shown by analyzing chances in expression profiles of miR-16, 181, 34a, and 125b in ‘normal’ clinical samples and ones with myelodysplastic syndrome. Reprinted from Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Vol. 70, Vaisocherová, H.; Šípová, H.; Víšová, I.; Bocková, M.; Špringer, T.; Laura Ermini, M.; Song, X.; Krejčík, Z.; Chrastinová, L.; Pastva, O.; Pimková, K.; Dostálová Merkerová, M.; Dyr, J. E.; Homola, J., Rapid and sensitive detection of multiple microRNAs in cell lysate by low-fouling surface plasmon resonance biosensor, pp. 226–231 (ref 95). Copyright 2015, with permission from Elsevier.