Figure 1.
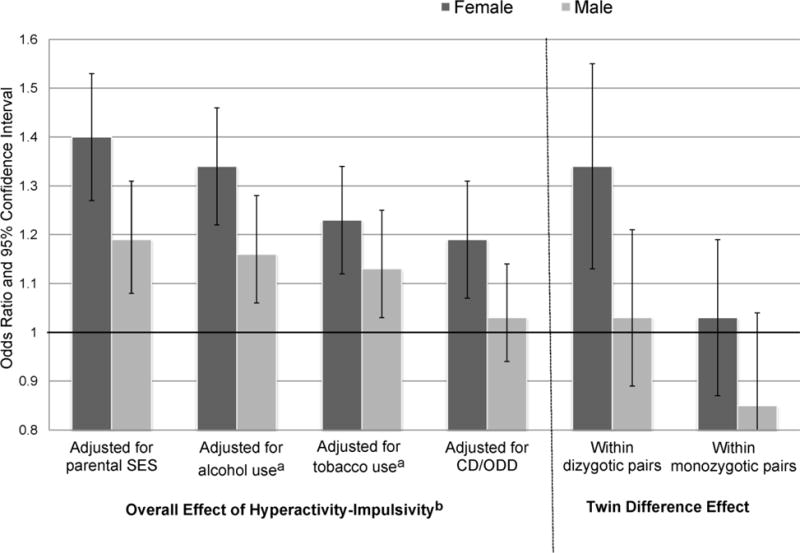
Overall Effects of ADHD Hyperactive-Impulsive Symptoms on Frequency of Marijuana Use, By Gender, Before and After Adjusting for Alcohol, Tobacco Use and Conduct/Oppositional Defiant Disorders, and Twin Difference Effects Within Dizygotic and Monozygotic Pairs
SES=socioeconomic status; CD/ODD=conduct/oppositional defiant disorder symptoms. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Marijuana frequency is coded: 0 = never; 1 = once a month or less; 2 = weekly/nearly weekly; 3 = daily/nearly daily. Odds ratios greater than 1 correspond to the increased odds of progressing one level of frequency to the next (i.e., from weekly to daily use) associated with each hyperactive-impulsive symptom. Twin difference effects reflect the differential likelihood of progressing in frequency associated with a twin having one more hyperactive-impulsive symptom than his or her co-twin.
aAdjusted for ever used alcohol or tobacco. When frequency of alcohol use was also considered, overall effects of hyperactivity-impulsivity remained significant for both genders (OR = 1.30 for females; 1.17 for males; p <.0001 and p = .001, respectively). When frequency of tobacco use was considered, only the overall effect for females remained significant (p<.05).
bOverall effect included N=3407 individuals; twin difference effects included 591 dizygotic or 1051 monozygotic pairs.
