Figure 2.
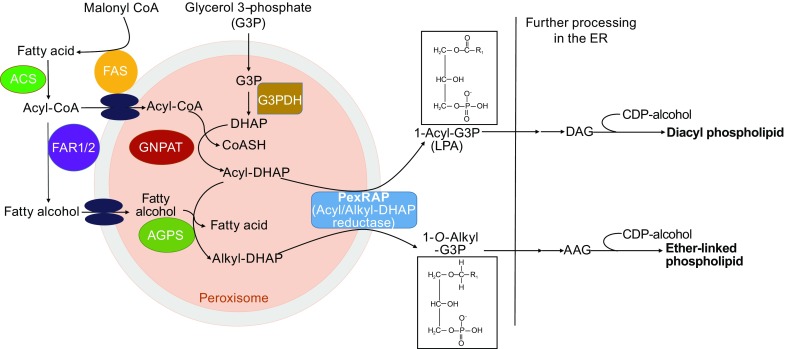
Acyl-DHAP pathway of ether lipid synthesis. This process begins in peroxisomes and is subsequently completed in the ER. The pathway utilizes dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) generated by glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PDH)-mediated dehydrogenation of G3P as the substrate for ether lipid synthesis. Fatty acid synthase (FAS)-mediated de novo lipogenesis generates fatty acyl-CoA that is utilized by glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase (GNPAT) or reduced to a fatty alcohol by a fatty acyl-CoA reductase (FAR1 or FAR2) to later be catalyzed by alkylglycerone phosphate synthase (AGPS), forming the ether bond and exchanging the acyl chain for an alkyl group. PexRAP (an acyl/alkyl DHAP reductase) then catalyzes the final peroxisomal step, generating the ether lipid precursors, 1-O-alkyl-G3P (AGP) or the diacyl phospholipid precursor lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). The completion of phospholipid synthesis occurs in the ER. This includes acylation of the glycerol backbone at the sn-2 position, converting LPA to diacylglycerol (DAG) and AGP to alkyl-acylglycerol (AAG), as well as addition of a cytidine diphosphate-alcohol head group (such as CDP-choline or CDP-ethanolamine) at the sn-3 position to form the mature phospholipid
