Figure 1.
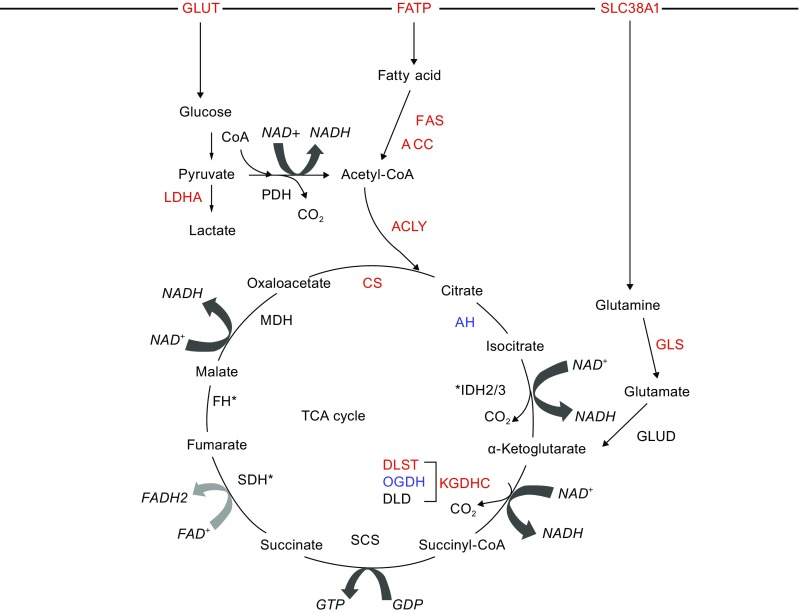
Transporters, fuels, enzymes, and biochemical reactions driving the TCA cycle. The typical input for the TCA cycle is acetyl-CoA, which is derived from pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis. Through a series of redox reactions, chemical bond energy from acetyl-CoA is harvested to produce high-energy electrons, which are carried to the electron transport chain by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). Subsequent oxidative phosphorylation results in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from each acetyl-CoA. Because oxygen is required to regenerate NAD+ and FAD, the TCA cycle only proceeds in aerobic environments. There are a total of 8 steps in the TCA cycle, three of which are irreversible; the generation of citrate from oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA by CS; the conversion of isocitrate to α-KG by IDH3; and the formation of succinyl-CoA from α-KG by KGDHC (Berg JM, 2002; Akram, 2014). The biochemical reactions in the TCA cycle are regulated by several means including substrate availability, product inhibition, and allosteric regulation, allowing the cell to control energy production based on its energy status (NADH/NAD+ ratio, ATP availability) and nutrient availability (Berg JM, 2002). Intermediates in the cycle can be derived from outside sources, such as the production of acetyl-CoA from β-oxidation of fatty acids or the production of α-KG from protein catabolism, particularly glutaminolysis (Houten and Wanders, 2010; Akram, 2014). Importantly, deregulation of TCA cycle enzymes, such as mutations and gene deregulations, or aberrant accumulation of TCA intermediates can have disease-relevant consequences. Proteins that are upregulated in cancer are highlighted as red and downregulated as blue, while enzymes mutated are marked with an asterisk. Abbreviations: CS: citrate synthase, AH: aconitase, IDH: isocitrate dehydrogenase, KGDHC: α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, OGDH: α-KG dehydrogenase, DLST: dihydrolipoamide S-succinyltransferase, DLD: dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, SCS: succinyl-CoA synthase, SDH: succinate dehydrogenase, FH: fumarate hydratase, MDH: malate dehydrogenase, PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase, GLUT: glucose transporter, FATP: fatty acid transporter, SCL38A: sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter, ACLY: adenosine triphosphate citrate lyase, ACC: acetyl-CoA carboxylase, FAS: fatty acid synthase, GLS: glutaminase, GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase
