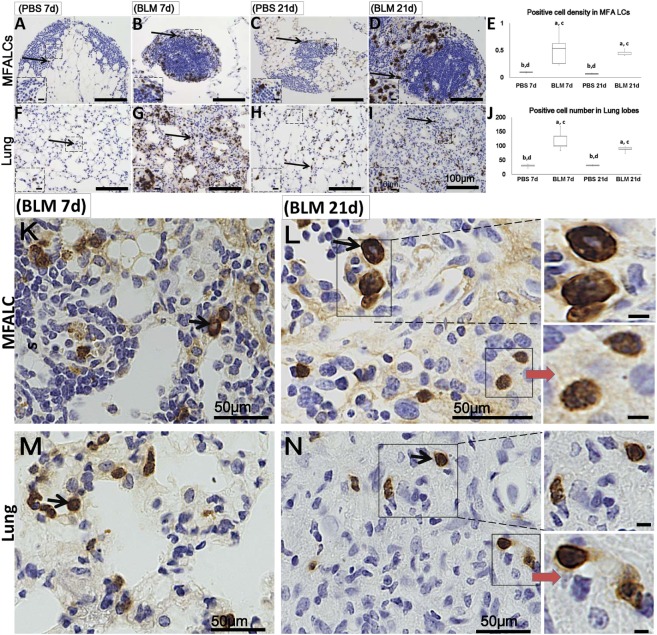
Figure 4.
Granulocyte cell populations within mediastinal fat-associated lymphoid clusters (LCs) (MFALCs) and lung infiltrates in mouse model of bleomycin (BLM)-induced pneumonitis. Immunohistochemical images (low-power) show Gr-1+ cells in MFALCs (A–D) and lung tissues (F–I) of PBS group at 7 days, BLM group at 7 days, PBS group at 21 days, and BLM group at 21 days, respectively. (E) Gr-1+ cell density in MFALCs. (J) Average number of Gr-1+ cells in lung tissues. The letters a, b, c, and d: significant differences between PBS group at 7 days (a), BLM group at 7 days (b), PBS group at 21 days (c), and BLM group at 21 days (d), analyzed by the Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by the Scheffé’s method (P < 0.05); n = 5 in each experimental group. Values = mean ± SE. Immunohistochemical images (high power) show Gr-1+ cell in MFALCs (K,L) and lung tissues (M,N) of BLM groups at 7 and 21 days post-instillation. Some cells showed lobulated nucleus with complete or incomplete rings, others showed smooth non-lobulated ring shaped nucleus with central basophilic cytoplasm (arrows).