Figure 2.
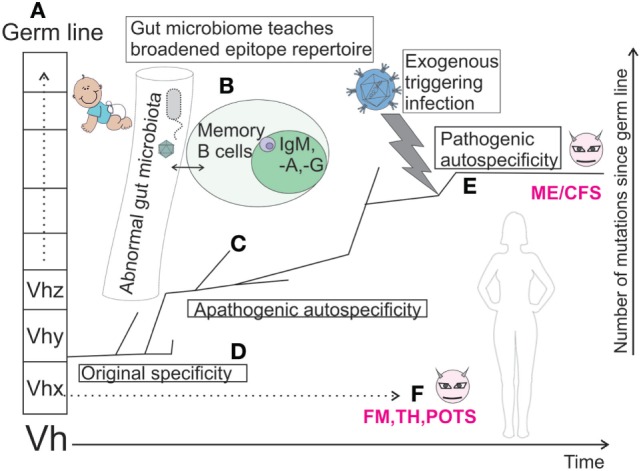
Mutational fate of a hypothetic germ line immunoglobulin heavy chain sequence (Vhy) in successive B cell clones, which gradually expand their paratope diversity in interplay with gut microbiota, T cells, and dendritic cells. If there is a chronic antigen stimulation, sequences more or less close to germ line sequence may be selected. Resulting B cells are stored as memory cells in germinal centers of gut-associated lymph nodes. Some of the developmental branches end due to clonal anergy or deletion (tolerization). Others are postulated to descend along a path to autospecificity due to an abnormality in gut commensal spectrum. An exogenous, triggering, antigenic stimulation (e.g., infection), eventually leads to overt pathogenic autospecificity (“evil” B cell clones, magenta) and ME/CFS. Similar fates of other B cell clones, which eventually turn autopathic and give comorbidities, are indicated under “F.” Characters A–F in bold refer to the stages mentioned under “Trying to place it under one umbrella.” This figure was inspired by work on the autoreactive clone VH4-34 (23, 24).
