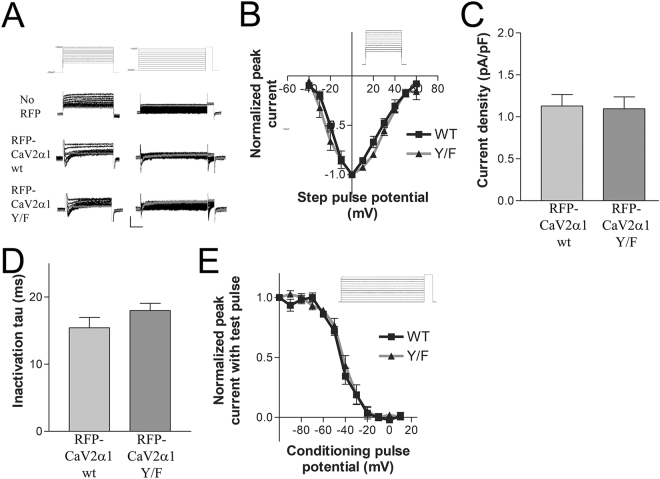
Figure 5.
Whole-cell currents from HEK293t cells expressing Aplysia RFP-CaV2α1 wildtype or RFP-CaV2α1 Y1501F, and CaVβ and CaVα2δ. (A) Representative traces from activation (left column) and steady-state inactivation (right column) voltage-clamp experiments. Top row are the command voltage steps overlaid, followed by the currents overlaid from representative cells without RFP, and RFP expressing cells transfected with either RFP-CaV2α1 wt or RFP-CaV2α1 Y1501F (along with CaVβ and CaVα2δ). The grey trace is the voltage step to −40 mV in the activation protocol and to 0 mV in the steady-state inactivation protocol, scale bars are 20 pA, 50/200 ms. (B) Activation curves generated from the protocol displayed in A for RFP-CaV2α1 (WT) and RFP-CaV2α1 Y1501F (Y/F) normalized to the peak current for each group. Data included only for cells with a larger peak inward current than outward current at the end of the step, to remove trials with larger residual potassium currents (n = 4,4). One trial from the Y1501F group was removed from the averaged data as an outlier at >10 pA/pF. (C) Comparison of mean current density between cells expressing RFP-CaV2α1 and RFP-CaV2α1 Y1501F (t-test P = 0.8632, n = 10,10). (D) Comparison of mean inactivation tau of peak currents between cells expressing RFP-CaV2α1 and RFP-CaV2α1 Y1501F (t-test, P = 0.1990, n = 10, 10). (E) Steady-state inactivation curves generated with 1 s conditioning pulses followed by a step to the test potential of + 20 mV comparing cells expressing either RFP-CaV2α1 (WT) or RFP-CaV2α1 Y1501F (Y/F) (n = 7,7).