Fig. 5.
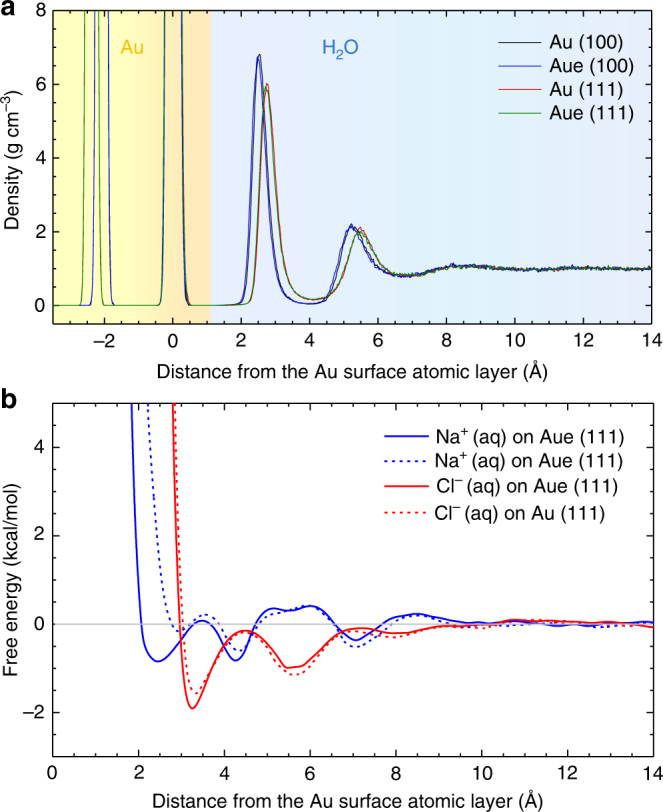
Density profile of water and free energy profiles of dissolved ions on the gold surface. a Computed density profile of water on the Au (111) and Au (100) surfaces with and without polarization. The difference between the polarizable and the nonpolarizable model is barely visible. Two distinct and two further weak surface layers of water are seen on both surfaces. Water molecules approach the top layer of the metal surface atoms 0.25 Å more closely on the (100) surface than on the (111) surface. b Computed free energy profile of sodium and chloride ions on the Au (111) surface in water with and without polarization. Polarization significantly changes preferred distances and adsorption energies of the ions, which is particularly visible for sodium ions at ~2.5 Å distance. Chloride ions exhibit different preferred distances compared to sodium ions and are more strongly attracted, enhanced at ~3.3 Å distance due to polarization. Adsorption energies are on the order of van-der-Waals contacts and weak hydrogen bonds. The zero point of the z coordinate corresponds to the position of the top layer of gold surface atoms in (a) and (b)
