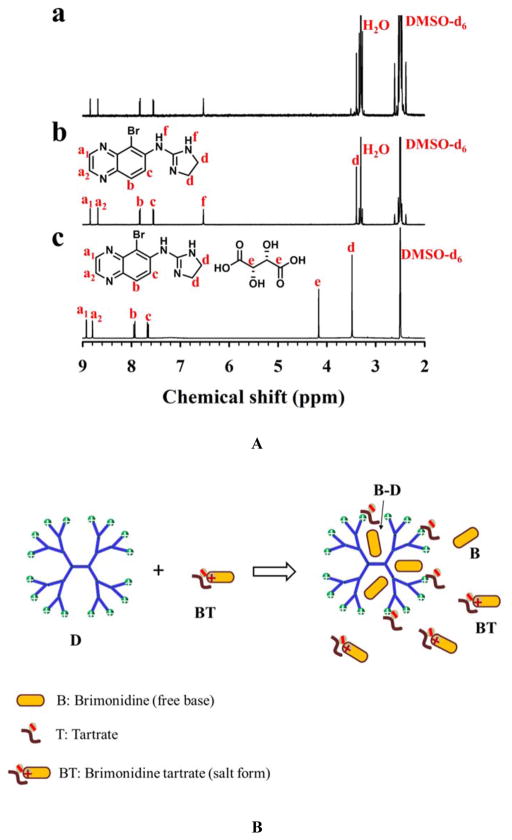
Figure 7.
Interactions of PAMAM dendrimers and brimonidine tartrate. (A) It is postulated that upon mixing, PAMAM dendrimer (D) unionizes brimonidine tartrate (BT), leading to formation of brimonidine free base (B) in the solution as well as entrapment of brimonidine free base into the dendrimer core (B–D) via hydrophobic interactions. Brimonidine exists in three forms: BT, B, and B–D in the presence of PAMAM dendrimer. (B) 1H NMR spectroscopy analysis confirms that PAMAM dendrimer converts brimonidine tartrate to brimonidine free base. a) 1H NMR spectrum of the precipitates resulting from mixing of brimonidine tartrate and PAMAM dendrimer G5, δ (ppm) 8.85 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 8.69 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.83 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (s, 2H), 3.40 (s, 4H) b) 1H NMR spectrum of brimonidine free base standard, δ (ppm) 8.85 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 8.69 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.83 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (s, 2H), 3.40 (s, 4H); and c) 1H NMR spectrum of brimonidine tartrate standard. δ (ppm) 8.93 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 8.80 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 4.17 (s, 2H), 3.48 (s, 4H).