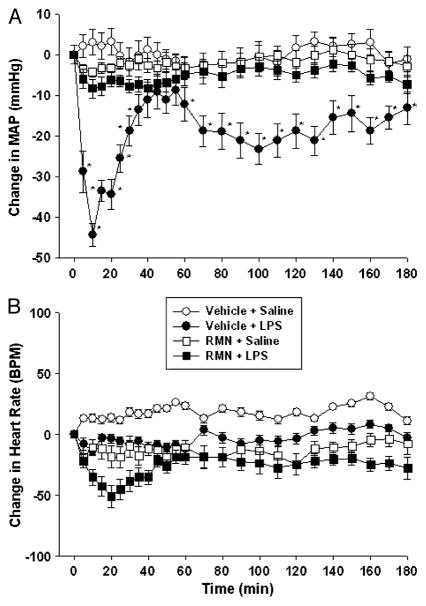
Fig. 2. Rimonabant (RMN) prevents the fall in arterial blood pressure induced by LPS in anesthetized rats.
Isoflurane-anesthetized rats were sequentially treated with intracerebroventricular rimonabant (250 ng) or saline, followed 2 min later by intravenous LPS (1 mg/kg) or saline, and MAP (upper panel) and heart rate (lower panel) were monitored for 180 min. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM change in MAP or heart rate. Baseline MAP and heart rate values were vehicle + saline (n = 6), 121.1 ± 6.2 mmHg and 352 ± 17 bpm; vehicle + LPS (n = 6), 118.8 ± 4.2 mmHg and 338 ± 22 bpm; RMN + saline (n = 6), 108.9 ± 4.9 mmHg and 366 ± 27 bpm; RMN + LPS (n = 6), 116.5 ± 5.1 mmHg and 347 ± 28 BPM. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated-measure ANOVA, followed by Tukey test. *P < 0.05, significantly different from saline-treated control animals.