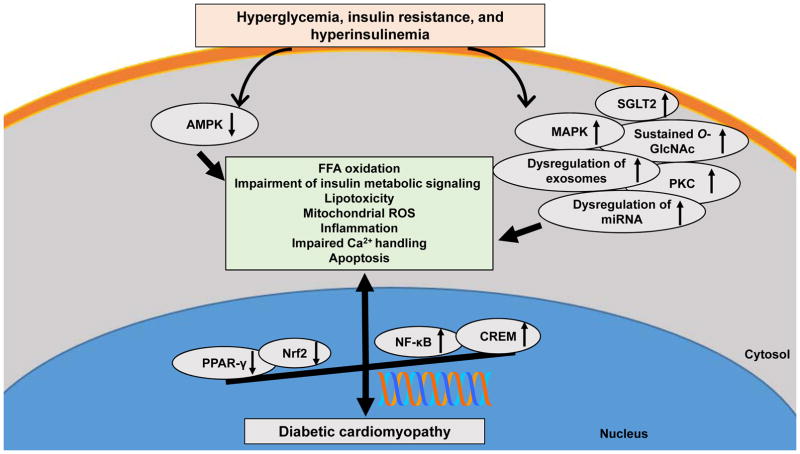
Fig. 2.
The molecular proteins and signaling pathways in hyperglycemia- and insulin resistance-diabetic cardiomyopathy. Increased PKC, MAPK, NF-κB, SGLT2, O-GlcNAc and CREM signaling, dysregulation of miRNA and exosomes, and reduction of AMPK, PPAR-γ and Nrf2 induce cardiac insulin resistance, subcellular component abnormalities, metabolic disorders, and structural changes, resulting in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Abbreviations: AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PKC, protein kinase C; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2; O-GlcNAc, O-linked N-acetylglucosamine; CREM, cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate-responsive element modulator; miRNA; microRNA.