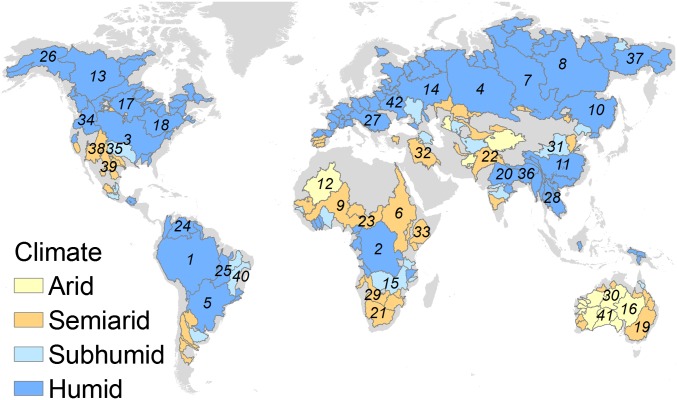
Fig. 1.
River basins (n = 186) examined in this study, with areas based on the Total Runoff Integrating Pathway (TRIP) database, with the 42 largest river basins (>500,000 km2) numbered and the associated aridity index (AI) based on the Koppen classification [14 basins in the arid class (AI: 0.0–0.2), 48 in the semiarid class (AI: 0.22–0.50), 20 in the subhumid class (AI: 0.50–0.65), and 104 in the humid class (AI > 0.65)]. The numbered river basins include the following: 1, Amazon; 2, Congo; 3, Mississippi; 4, Ob; 5, Parana; 6, Nile; 7, Yenisei; 8, Lena; 9, Niger; 10, Amur; 11, Yangtze; 12, Tamanrasset; 13, MacKenzie; 14, Volga; 15, Zambezi; 16, Lake Eyre; 17, Nelson; 18, St. Lawrence; 19, Murray; 20, Ganges; 21, Orange; 22, Indus; 23, Chari; 24, Orinoco; 25, Tocantins; 26, Yukon; 27, Danube; 28, Mekong; 29, Okavango; 30, Victoria; 31, Huang He (Yellow River); 32, Euphrates; 33, Jubba; 34, Columbia; 35, Arkansas; 36, Brahmaputra; 37, Kolyma; 38, Colorado; 39, Rio Grande; 40, Sao Francisco; 41, Nullarbor; and 42, Dnieper (SI Appendix, Table S3).