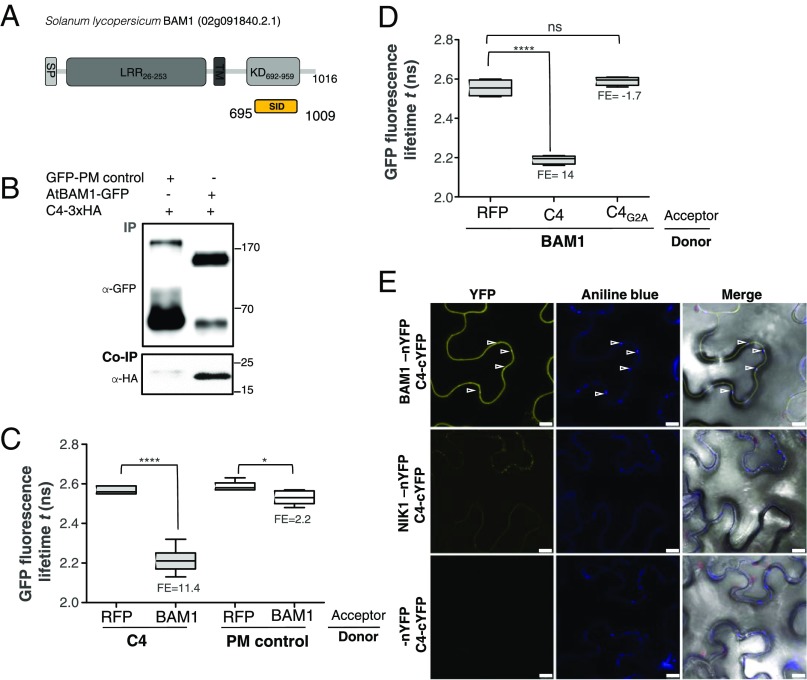
Fig. 2.
C4 interacts with the receptor-like kinase BAM1. (A) Schematic representation of the receptor-like kinase BAM1 from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) isolated in the yeast two-hybrid screen as an interactor of C4. The signal peptide (SP), leucine-rich repeats (LRR), transmembrane domain (TM), and kinase domain (KD) are shown; numbers indicate the beginning and end of each domain, in amino acids. The selected interaction domain (SID) is the minimal fragment found to interact with C4 in this screen. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of BAM1-GFP from Arabidopsis with C4-3xHA upon transient coexpression in N. benthamiana leaves. Numbers on the right indicate molecular weight. (C) Interaction between C4 and BAM1 by FRET-FLIM upon transient coexpression in N. benthamiana leaves. The membrane protein NP_564431 (NCBI) is used as a negative control (PM control). FE, FRET efficiency. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference (****, P value < 0.0001; *P value < 0.05), according to a Student’s t test. (D) Interaction between BAM1 and C4 and BAM1 and C4G2A by FRET-FLIM upon transient coexpression in N. benthamiana leaves. FE, FRET efficiency. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference (****, P value < 0.0001), according to a Student’s t test. (E) Interaction between C4 and BAM1 by BiFC upon transient coexpression in N. benthamiana leaves. The receptor-like kinase NIK1 is used as a negative control. Arrowheads indicate plasmodesmata. (Scale bar, 10 µm.)