Figure 1. Summary of early of neural development events regulated by Wnt signaling.
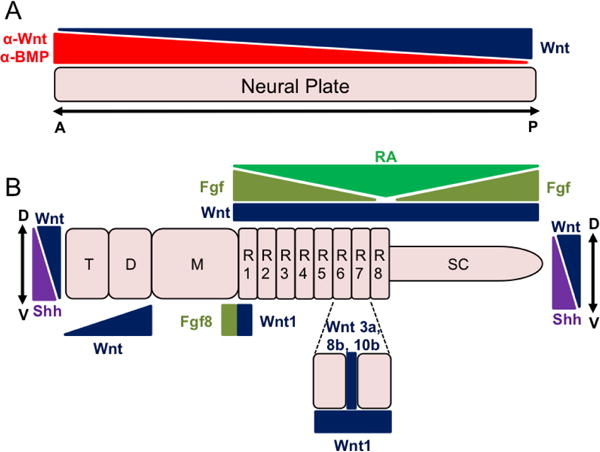
A. The neural plate initially emerges from the ectoderm through the action of BMP antagonists (α-BMPs). Opposing gradients of Wnt antagonists (α-Wnt) and Wnt ligands pattern the neural tube along the anterior-posterior (A/P) axis. B. As the neural tube continues to mature, it becomes further subdivided into primary vesicles (prosencephalon, mesencephalon [M], and the rhombencephalon) and the developing spinal cord (SC). The prosencephalon will be further divided into the telencephalon (T) and diencephalon (D). In addition, the rhombencephalon dives into eight rhombomeres (R1-R8). Wnt signaling along with other signaling molecules (e.g. FGFs, Shh, retinoic acid [RA]) regulates the further patterning and maturation of these regions along both the A/P as well as dorsal-ventral (D/V) axis.
