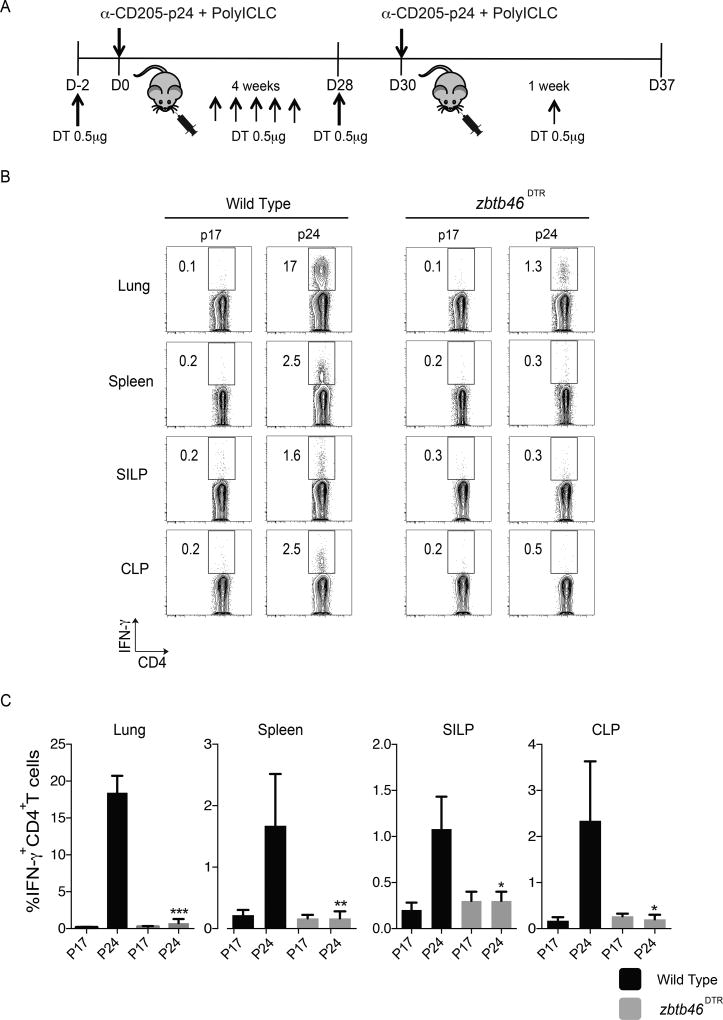
Figure 3. Classical DCs are essential for inducing systemic and mucosal immune responses to intranasal immunization.
Wild type (WT) and zbtb46DTR mice were immunized i.n. with α–CD205-p24 fusion mAb (5µg) and poly ICLC (50µg) in a prime-boost manner. Diphtheria toxin (DT), (0.5µg) was administered i.p., 48 hours prior to immunization and every five days post vaccination. Additional doses of DT were administered on day 28 and 4 days post-boost. IFN-γ secretion in response to HIV gag p24 (immunizing) or p17 (control) peptide pools was evaluated one week post-boost by intracellular cytokine staining.
(A) Shows the schema of immunization
(B) FACS plots from a representative experiment, illustrating the induction of IFN-γ+CD4+ cells in the lung, spleen, SILP and CLP.
(C) Mean data from three independent experiments (5 mice per group) is shown. Statistical comparisons between p24 levels in WT and zbtb46DTR mice are shown. Error bars show mean ± SD. *=p<0.05, **=p<0.01, ***=p<0.001