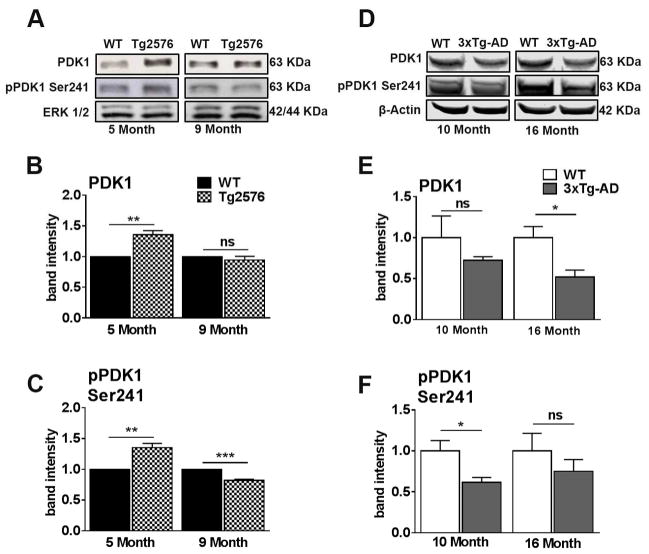
Figure 4. PDK1 activity is dysregulated prior to the onset of peripheral insulin resistance in Tg2576 and 3xTg-AD mice.
(A) Representative western blots of protein extracted from both 5- and 9-month-old Tg2576 and WT mice. Blots were probed with the indicated antibodies. (B) PDK, a downstream kinase of insulin receptor activation, was up regulated in 5-month-old Tg2576 (t (10) = 5.13, p < 0.01), but not 9-month-old compared to WT. (C) pPDK is up regulated in 5-month-old and downregulated in 9-month-old Tg2576 mice compared to WT mice (t (10) = 5.13, p < 0.01 and t (10) = 8.647, p < 0.001 for 5- and 9-month-old, respectively). (D) Representative western blots of protein extracted from both 10- and 16-month-old 3xTg-AD and WT mice. (E) 10-month-old 3xTg-AD mice show no significant differences in total PDK1 levels compared to age-matched WT mice. At 16 months of age, 3xTg-AD mice show a significant reduction in total PDK levels compared to WT mice (t (10) = 8.987, p < 0.05). (F) 10-month-old 3xTg-AD mice show a significant reduction of pPDK1 at Ser 241 compared to age-matched WT mice (t (10) = 7.722, p < 0.05). No significant difference for 16-month-old 3xTg-AD mice. Quantitative analyses of the blots obtained by normalizing the quantity of a specific protein with its loading control. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. n = 6/genotype/age.