Figure 2.
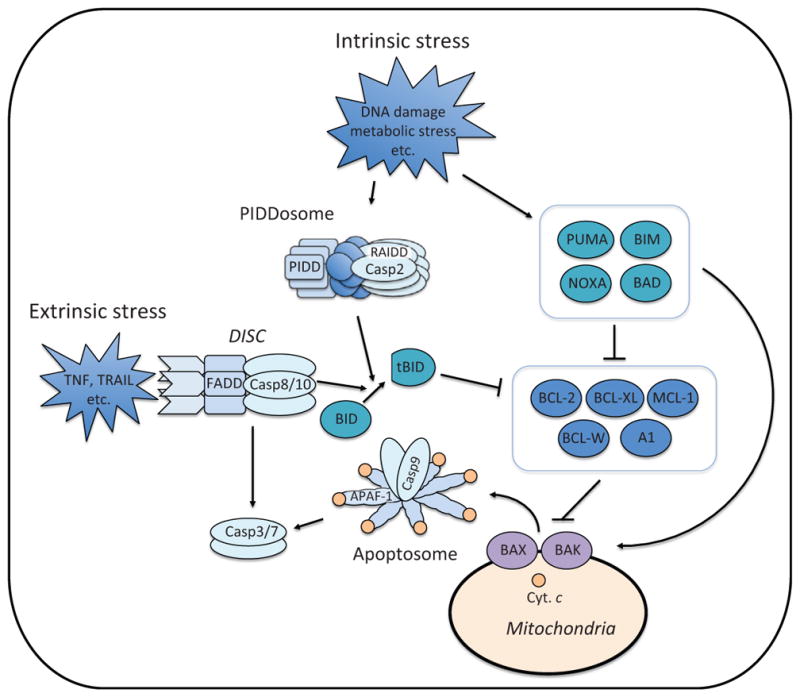
Apoptosis pathways. Intrinsic stress (e.g., DNA damage and metabolic stress) induces the expression and/or activation of proapoptotic BH3-only proteins, which either suppress antiapoptotic BCL-2 family proteins or directly activate BAX and BAK (Fig. 3). BAX and BAK induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Upon MOMP, cytochrome c (Cyt. c) is released from the mitochondrial intermembrane space. The release of cytochrome c triggers the formation of apoptosome in the cytoplasm, which recruits and activates caspase-9. Active caspase-9 cleaves and activates effector caspases, caspases-3 and -7. Intrinsic stress also engages the formation of PIDDosome which is composed of PIDD, RAIDD, and caspase-2. Through proximity-induced activation, casapse-2 becomes active and cleaves BID. Once cleaved, BID (tBID: truncated BID) becomes an active BH3-only protein. Extrinsic stress (e.g., TNF and TRAIL) is mediated through the death receptor, which forms the DISC (Death Inducing Signaling Complex) with FADD and caspase-8. Active caspase-8 directly cleaves and activates effector caspases or triggers the intrinsic apoptosis pathway through BID cleavage. TNF; tumor necrosis factor, TRAIL; TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
