Figure 9.
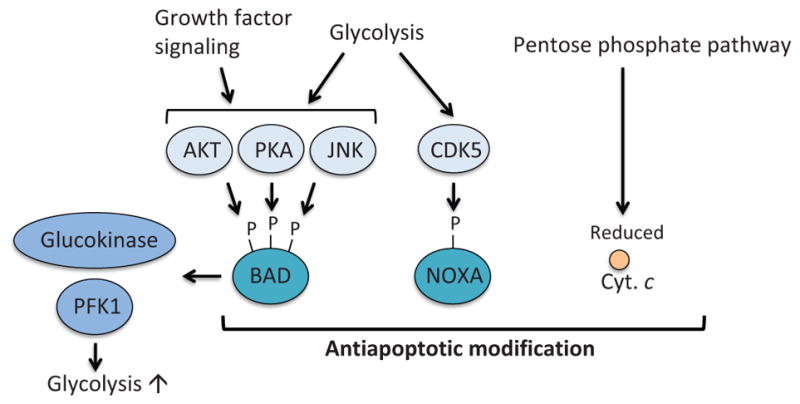
Metabolism-mediated modification of pro-apoptotic proteins. BAD is phosphorylated by AKT, PKA, and JNK that are regulated by glycolysis and growth factor signaling. Phosphorylation of BAD results in suppression of the antiapoptotic functions of BAD. Moreover, phosphorylated BAD contributes to activation of glucokinase and PFK1, therefore enhancing the glycolysis pathway. Atypical cyclin-dependent kinase, CDK5, is activated by glycolysis. Active CDK5 phosphorylates and inhibits the BH3-only protein NOXA. The pentose phosphate pathway produces NADPH, which also controls redox state of cytochrome c and suppresses apoptosome formation and apoptosis. PKA; protein kinase A, JNK; c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, CaMKII; calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase II.
