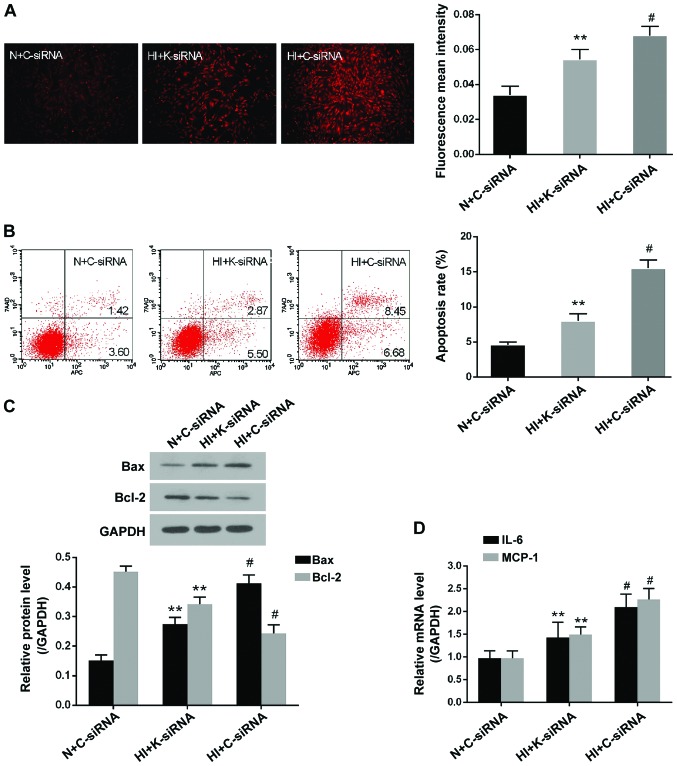
Figure 4.
KDM3A knockdown decreases reactive oxygen species generation, cell apoptosis and inflammation in high insulin-treated VSMCs. (A) Representative fluorescent images of dihydroethidium staining post-transduction with lenti-K-siRNA or lenti-C-siRNA (magnification, ×100) (left panel). Fluorescent mean density measured by ImageJ software (right panel). (B) Representative flow cytometry plots of the effects of KDM3A inhibition on high insulin-induced cellular apoptosis (left panel). Relative apoptosis rates post-transduction with lentiviruses (right panel). (C) Representative immunoblots for Bax and Bcl-2 expression post-transduction with lenti-K-siRNA or lenti-C-siRNA (upper panel). Densitometric analysis of western blotting (lower panel). (D) Effects of KDM3A inhibition on the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and MCP-1 in VSMCs. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation, n=3. **P<0.05 vs. the HI + C-siRNA group; #P<0.05 vs. the N + C-siRNA group. Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; C-siRNA, control siRNA; HI, high concentration insulin stimulation; IL-6, interleukin-6; KDM3A, lysine (K)-specific demethylase 3A; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; K-siRNA, KDM3A siRNA; N, normal medium; siRNA, small interfering RNA; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells