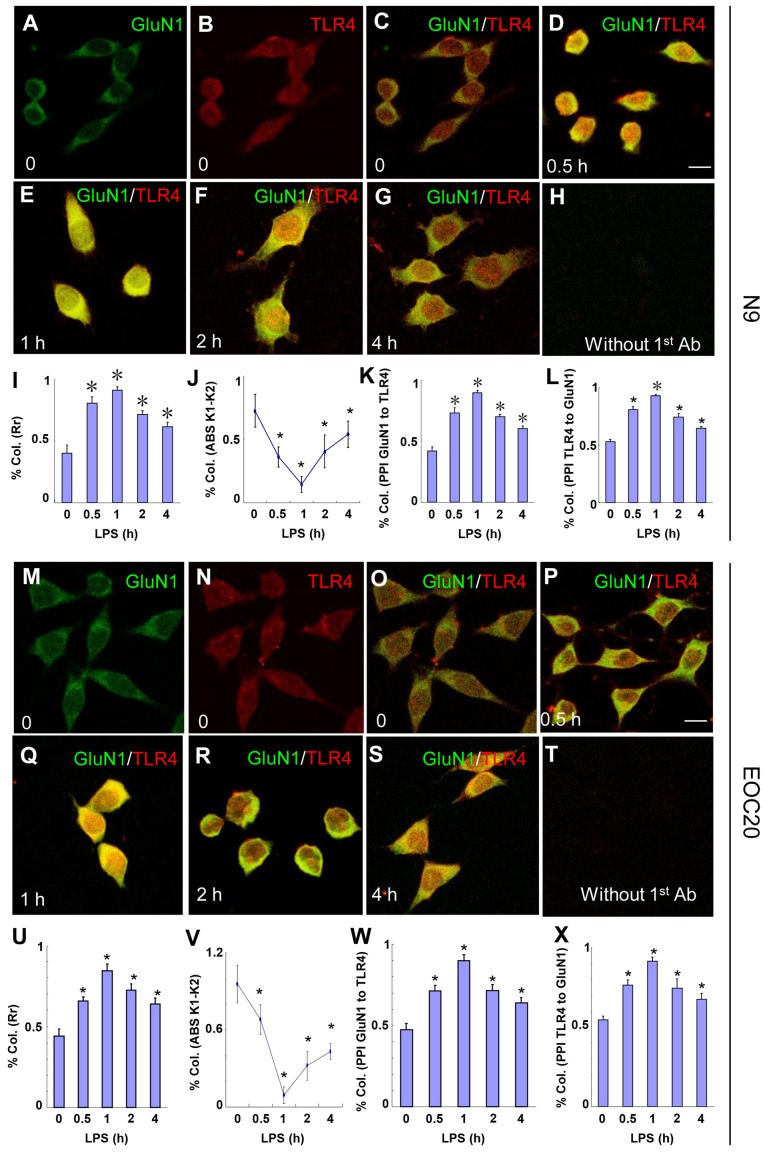
Figure 2.
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and glutamate receptor N-methyl-D-aspartate subunit 1 (GluN1) co-localize in N9 and EOC 20 microglial cells. (A–L) N9 and (M–X) EOC 20 microglial cells were treated with 1 µg/ml LPS for (D and P) 30 min, (E and Q) 1 h, (F and R) 2 h or (G and S) 4 h, and stained for GluN1 (green) and TLR4 (red). Without LPS treatment, (C and O) no co-localization of TLR4 and GluN1 was observed. Single GluN1 and TLR4 images are shown in (A and M) and (B and N), respectively, in the group without LPS treatment. No signal was observed if TLR4 and GluN1 antibodies were replaced with goat IgG and rabbit IgG, respectively. Five to ten fields from each condition were randomly selected and analyzed with CoLocalizer Pro software and Protein Proximity Analysis software. The results are shown in (I–L) for N9 and (U–X) for EOC 20 microglial cells. *P<0.05 vs. 0 (without LPS treatment). Scale bar, 20 µM. The experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results, and two coverslips were examined for each condition in one test (n=6). Col., colocalization; Rr, Pearson's correlation coefficient; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.