Figure 4. CL enhances the ATPase activity of COQ8 and liposome binding.
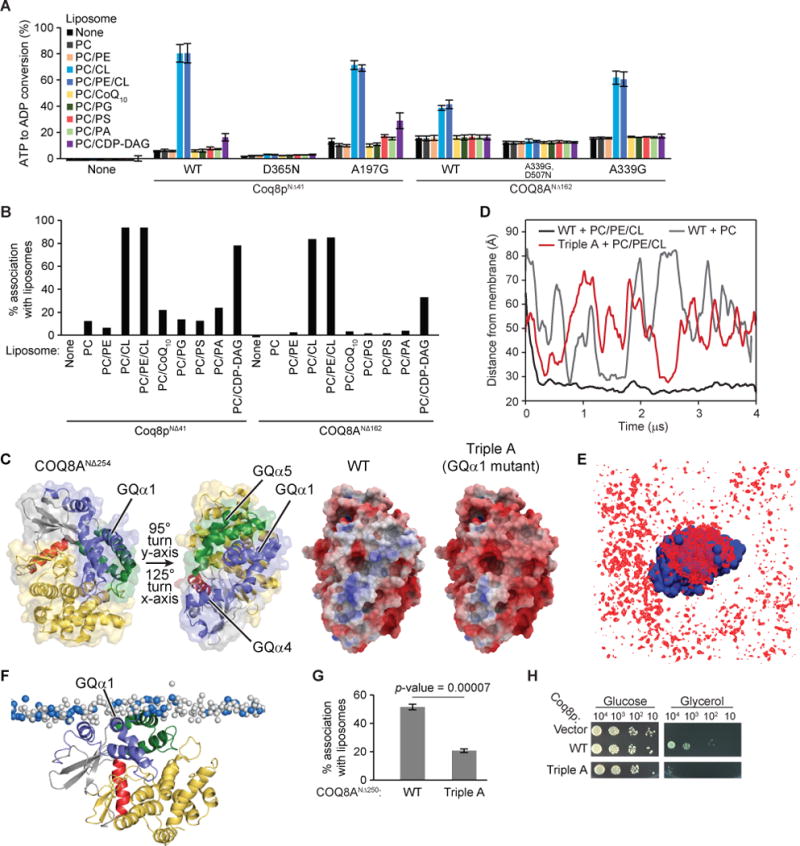
(A) ADP-Glo assay with a panel of liposomes and TM domain containing COQ8. Error bars represent s.d. of two independent experiments performed in technical duplicate. (B) Liposome flotation assay with a panel of PC based liposomes and TM-containing COQ8. (C) The two structures of COQ8ANΔ254 on the left are colored according to Stefely et al., 2015 and turned to show the orientation of the electrostatic maps. The KxGQ domain is colored in purple and green in the structures on the left. On the right, there are electrostatic maps of COQ8ANΔ254 showing the positively charged region spanning GQα1, GQα4, and GQα5 [negative (−5 kcal/e.u. charge): red, via white, to positive (+5 kcal/e.u. charge): blue]. (D) Time evolution of the distance between the center of mass of the protein and the center of mass of the phosphate heads of the leaflet it interacts with for CG-MD simulations of COQ8ANΔ254 with PC or PC/PE/CL liposomes or of the Triple A mutant with PC\PE\CL liposomes. (E) Average occupancy of CL phosphate heads (red) when COQ8ANΔ254 (blue) is centered throughout the trajectory. (F) Snapshot from a CG-MD simulation (t ~ 4 μs) showing the interaction of COQ8ANΔ254 with a PC/PE/CL membrane. CL phosphate heads shown in blue and PC/PE phosphate heads shown in white. (G) Percent protein associating with liposomes from a liposome flotation assay with COQ8ANΔ250 WT and the Triple A mutant (R262A,R265A,K269A). (H) Serial dilutions of Δcoq8 transformed with Coq8p WT or the Triple A mutant (R120A,K124A,K127A) on synthetic complete glucose (2% w/v) or glycerol (3% w/v) containing media. See also Figure S4.
