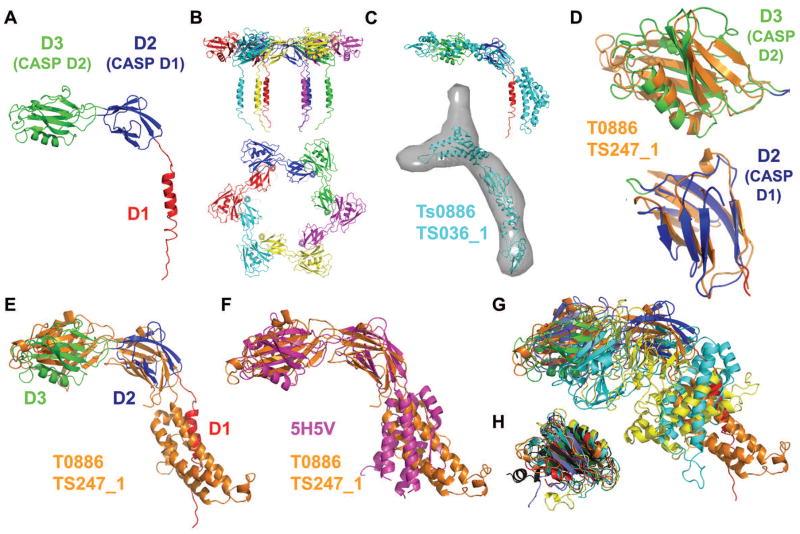
Figure 1. (A) Crystal structure of the Pseudomonas FliD78-405 monomer subunit.
in which the domain D3 (CASP domain D2, green), domain D2 (CASP domain D1, blue) and the helical region (red), which belongs to domain D1 (not evaluated in CASP), are indicated. (B) Side view (top panel) and top view (bottom panel) showing cartoon representations of the hexameric FliD78-405 crystal structure. Each monomer subunit is colored distinctly. (C) SAXS-generated molecular envelope of the monomeric FliD1-474 with the CASP prediction model T0886TS036_1 (cyan). (D) Superposition of CASP prediction models T0886TS247_1_D1 (orange) and T0886TS247_1_D2 (orange) with D2 (CASP domain D1, blue) and D3 (CASP domain D2, green) of the FliD78-405 monomer crystal structure. (E) Superposition of CASP prediction model T0886TS247_1 (orange) with the FliD78-405 monomer crystal structure (domain coloring as in Panel A). (F) Superposition of CASP prediction model T0886TS247_1 (orange) with the E. coli FliD43-416 crystal structure 5H5V (magenta). (G) Superposition of CASP prediction models T0886TS247_1 (orange), T0886TS011_1 (cyan), T0886TS064_1_1 (light blue), T0886TS411_1 (yellow) with the FliD78-405 monomer crystal structure (domain coloring as in Panel A). (H) Superposition of CASP prediction models T0886TS247_1-D2 (orange), T0886TS064_1_1-D2 (light blue), T0886TS011_1-D2 (cyan), T0886TS411_1-D2 (yellow), T0886TS456_1-D2 (dark grey), T0886TS173_1_1-D2 (red) with D3 of the FliD78-405 monomer crystal structure (green).