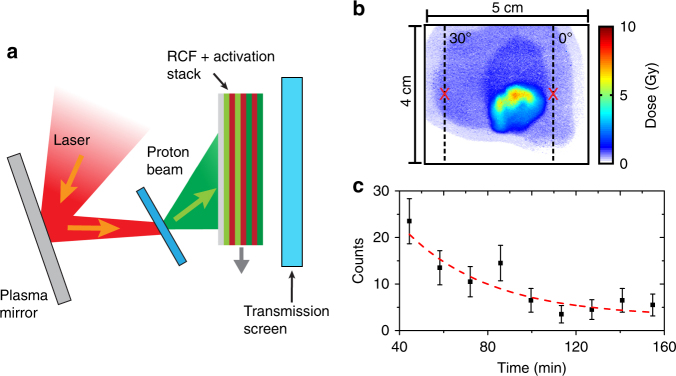
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the experiment set-up and example measurements. a A pulse from the Vulcan laser is focused by an f/3 off-axis parabola and reflected from a planar plasma mirror onto a target foil. The spatial-intensity profile of the beam of accelerated protons is measured using stacked dosimetry film (RCF), interwoven with Cu foils for nuclear activation measurements. The transmitted laser energy is characterised on a transmission screen (with the stack retracted). b Example proton beam dose distribution, as measured using RCF, for proton energies εp ≥ 89 MeV. The red markers at 0° and 30° correspond to the laser axis and target normal axis, respectively. c Example measurements of the positron-emission decay of the 63Zn radioisotope produced by proton activation of Cu in the stack (63Cu(p,n)63Zn), for protons with εp > 92 MeV. The time is measured from the time of the laser-plasma interaction and the error bars are determined from the statistical uncertainties in the measured counts. The dashed curve is a fit corresponding to the 38.5 min half-life of 63Zn, confirming proton-induced activation in the high-energy region of the filter stack