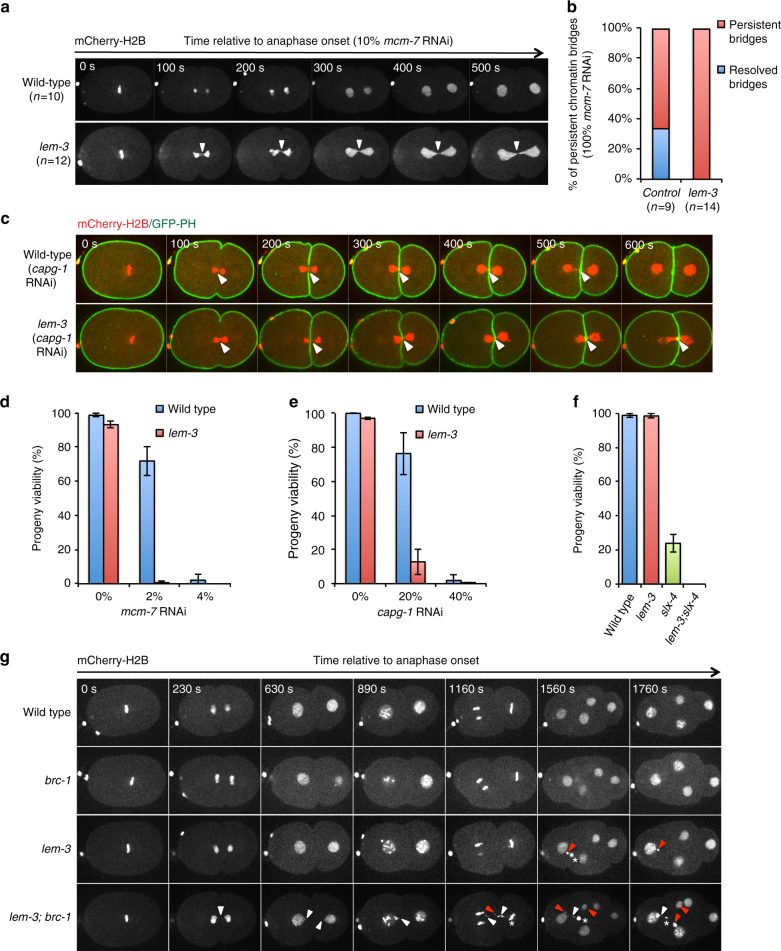
Fig. 3.
LEM-3 contributes to chromatin-bridge resolution. a Chromosome segregation in wild type and lem-3 mutant embryos upon partial depletion of DNA replication helicase subunit MCM-7. Images were taken from embryos expressing mCherry-H2B fed on 10% mcm-7 RNAi producing bacteria. Arrowheads indicate chromatin bridges. Times are relative to anaphase onset of the first division. b Quantification of chromatin bridges that persist into the next cell division in wild type and lem-3 mutant embryos upon full depletion of MCM-7 (100% mcm-7 RNAi). n sample size. c Persistent capg-1 RNAi induced chromatin bridges in lem-3 mutants. Chromosome segregation in wild type and lem-3 mutant embryos upon depletion of condensin I subunit CAPG-1 (100% capg-1 RNAi). Images were taken from control and capg-1 RNAi embryos expressing mCherry-H2B and GFP-PH. d, e Progeny viability of lem-3 mutants upon partial depletion of MCM-7 (d) and CAPG-1 (e). f Genetic interaction between LEM-3 and SLX-4. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean. g LEM-3 and BRC-1 are required for faithful chromosome segregation after IR. White arrowheads indicate chromosome bridges, red arrowheads indicate micronuclei. Stars indicate polar bodies