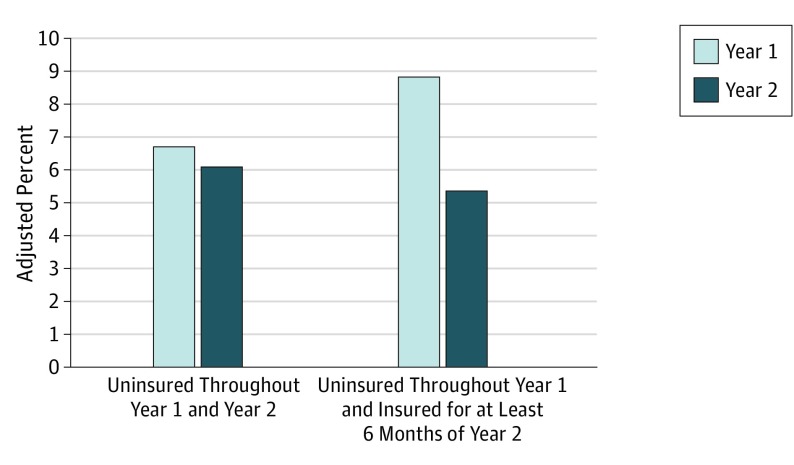
Figure 2. Unmet Need for Prescription Drugs Among Adults Uninsured Throughout Year 1.
Estimates from multivariable linear probability model controlling for the effects of age, sex, and race/ethnicity in year 1 and time-varying measures of household income as a percentage of the federal poverty line, self-reported health, and number chronic conditions (coronary heart disease, angina, myocardial infarction, other heart disease, stroke, emphysema, high cholesterol, diabetes, arthritis, and asthma). Decrease in unmet need for those gaining health insurance in Year 2 was significantly greater than for the continuously uninsured.