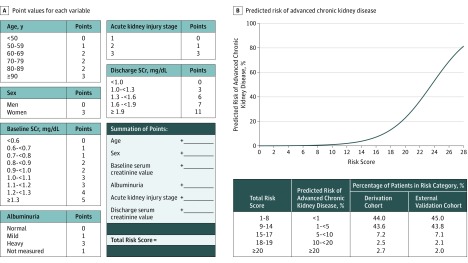
Figure 2. Six-Variable Risk Index for Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease Following Hospitalization With Acute Kidney Injury.
Acute kidney injury stage 1 is defined by serum creatinine (SCr) increase of 0.3 mg/dL or more or 1.5 to 1.9 times the baseline within index hospitalization; stage 2, serum creatinine increase of between 2.0 and 2.9 times baseline within index hospitalization; stage 3, serum creatinine increase of 3.0 mg/g or more times baseline or 4.0 mg/dL or more within index hospitalization. Normal albuminuria is indicated by an albumin:creatinine ratio (ACR) of 30 or less or a dipstick negative urinalysis protein; mild, ACR of 30 mg/g to 300 mg/g or dipstick positive urinalysis protein trace or 1+; heavy, ACR of more than 300 mg/g or dipstick positive urinalysis protein of 2+ or more. To convert urine ACR to mg/mmol, multiply by 0.113.
Points assigned to values of each variable can be summed to obtain a patient’s total risk score, which can be used to determine his/her corresponding predicted risk of developing advanced chronic kidney disease (Supplement 2). A smartphone app is available on Calculate by QxMD for iOS, Android, and Windows (free install at https://qxmd.com/getcalculate).