FIG 3.
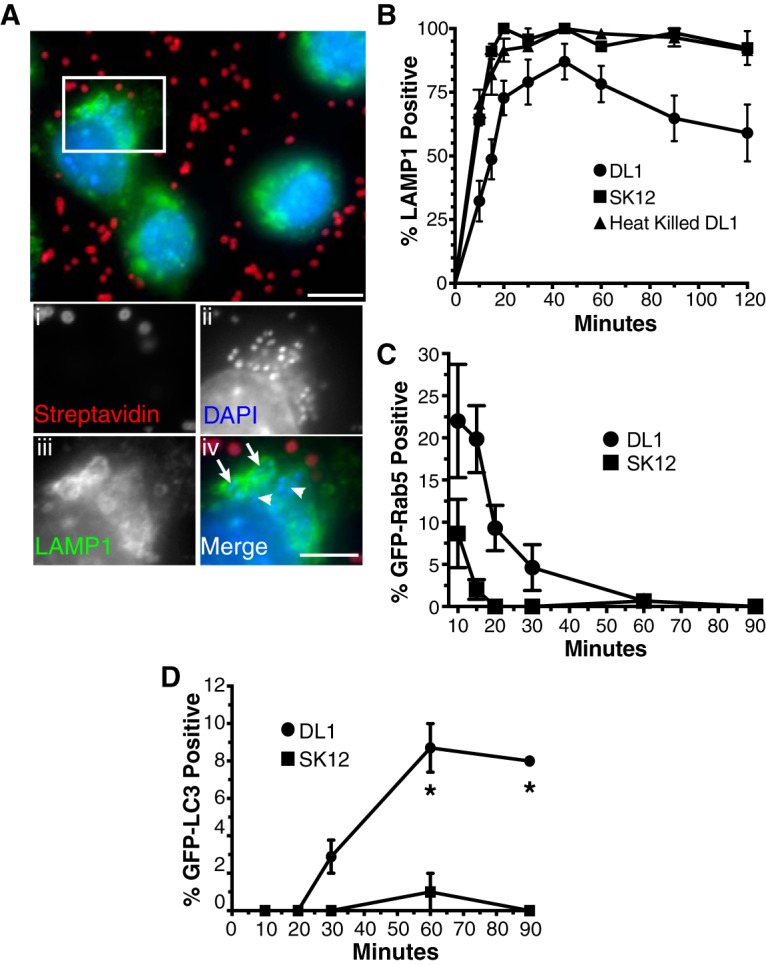
Phagosomes containing S. gordonii DL1 exhibit altered maturation profiles. (A and B) The rates of LAMP1 acquisition by phagosomes containing S. gordonii were determined by immunofluorescence staining and quantification following synchronized phagocytosis. (A) Example immunofluorescence images of LAMP1-positive (arrows in panel iv) and -negative (arrowheads in panel iv) phagosomes containing engulfed S. gordonii (streptavidin negative). Bar = 10 μm (5 μm in panel iv). (B) Percentage of LAMP1-positive S. gordonii-containing phagosomes versus time postengulfment. Heat-killed DL1- and live SK12-containing phagosomes all quickly acquired LAMP1, while, on average, fewer than 80% of phagosomes containing live DL1 obtained the phagolysosomal marker over 120 min. Data shown are means ± standard errors for at least 4 independent experiments per condition, with a minimum of 50 phagosomes per time point per experiment examined. The LAMP1 acquisition curves for DL1 versus SK12 and heat-killed DL1 are significantly different by one-phase association fitting (P < 0.001). (C and D) Synchronized phagocytosis of S. gordonii was performed with RAW264.7 macrophages transfected with GFP-Rab5 (C) or GFP-LC3 (D), and quantification of marker-positive S. gordonii-containing phagosomes over time was performed. Data shown are mean percentages ± standard errors for at least 3 independent experiments, with a minimum of 50 phagosomes per time point per experiment examined. (C) The rates of GFP-Rab5 loss from DL1- and SK12-containing phagosomes are significantly different by one-phase decay fitting (P < 0.001). (D) Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.01) in GFP-LC3 labeling at individual time points by unpaired t test, using the Holm-Sidak method for multiple comparisons.
