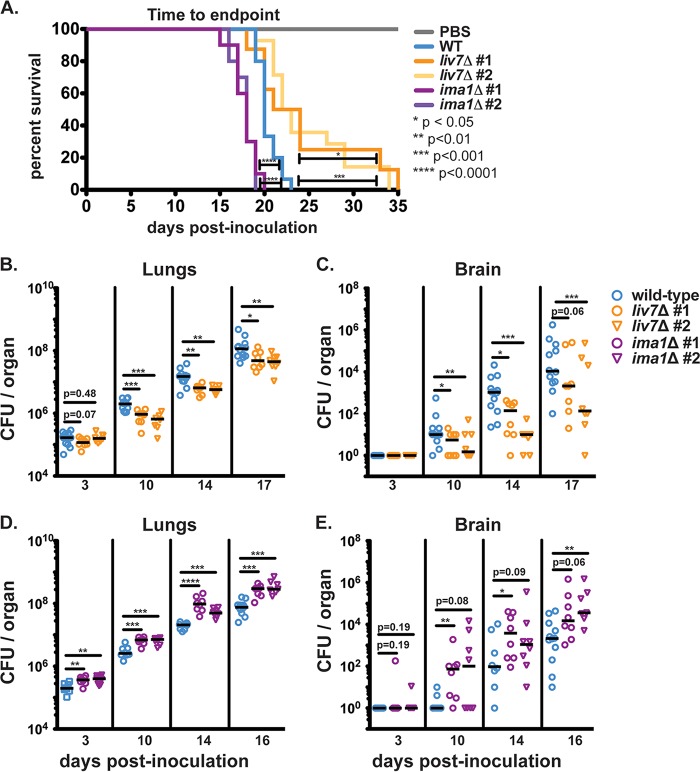
FIG 5.
Mutants' alterations to in vitro exo-GXM release correlate with changes in survival and fungal burden during infection. (A) C57BL/6NJ mice inoculated intranasally with ima1Δ mutant 1/2 (n = 10 for both) reach endpoint significantly sooner than wild-type-infected mice (n = 15). Wild-type-infected mice reached endpoint sooner than liv7Δ mutant 1/2-infected mice (n = 8 and n = 14, respectively). Mock-infected animals given sterile 1× PBS (n = 5) did not show signs of disease 35 days postinoculation. P values were calculated using a log rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (B) liv7Δ mutant 1/2-infected mice (n = 8 for both) show decreased lung burden beginning at 10 days postinoculation compared to the wild-type level (n = 12). (C) Brain fungal burden is significantly lower in liv7Δ mutant 1/2-infected animals than wild-type-infected animals. (D) Lung fungal burden is significantly higher in ima1Δ mutant 1/2-infected mice (n = 8 for both) than in wild-type-infected mice (n = 8 on days 3, 10, and 14; n = 12 on day 16) beginning at least 3 days postinoculation. (E) Dissemination to the brain trends higher in ima1Δ mutant 1/2-infected mice. P values were calculated using a Mann-Whitney test.