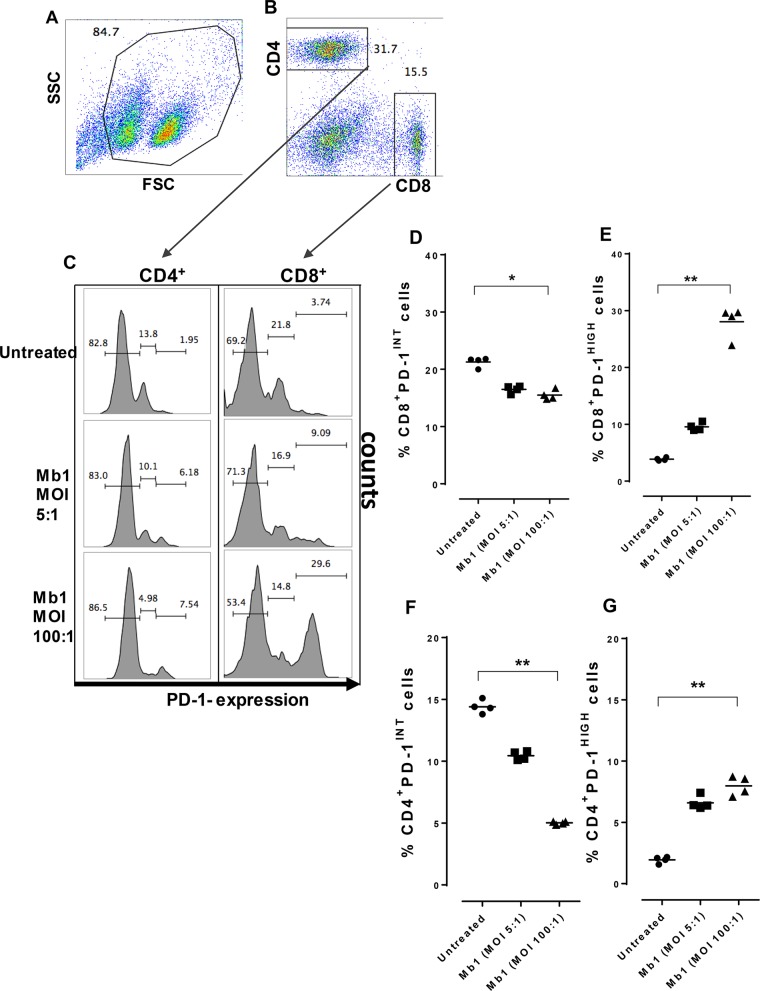
FIG 5.
PD-1INT T-cell subsets function as progenitor pools for PD-1HIGH T-cell subsets. The pools of exhausted T cells were analyzed to identify pre- and postinfection changes in CD4+ PD-1INT and CD8+ PD-1INT subsets and also CD4+ PD-1HIGH and CD8+ PD-1HIGH subsets. (A and B) PBMCs were gated and sorted to study CD4+ and CD8+ T cells for PD-1 expression after 18 h of incubation with or without M. bovis at different MOIs. (C) Results showing percentages of PD-1 expression on CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the control and after Mb1 infection at MOIs of 5:1 and 100:1 in distinct intermediate and high subsets based on PD-1 expression. (D) Significant decrease in the percentages of CD8+ PD-1INT cells after Mb1 infection (MOI of 100:1) (**, P < 0.05). (E) Significant increase in the percentages of CD8+ PD-1HIGH cells after Mb1 infection (MOI of 100:1) (**, P < 0.01). (F) Significant decrease in the percentages of CD4+ PD-1INT cells after Mb1 infection (MOI of 100:1) (**, P < 0.01). (G) Significant increase in the percentages of CD4+ PD-1HIGH cells after Mb1 infection (MOI of 100:1) (**, P < 0.01). Three technical replicates were always performed under every condition in each experiment, and the graphs indicate the medians and ranges of representative data from one of three independent experiments (four animals in each experiment).