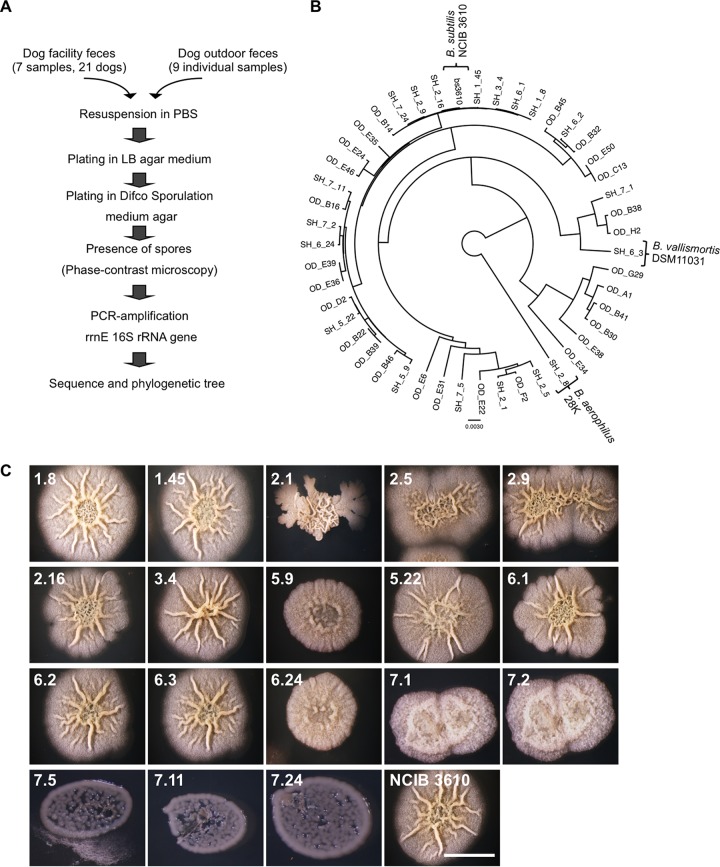
FIG 1.
Bacillus subtilis is present in the dog intestinal microflora. (A) Schematic representation of the procedure used to sequence the 16S rrnE gene from sporulating bacteria isolated from the feces of dogs of the UZH animal facility and privately owned dogs. (B) Bayesian phylogeny of the 16S rrnE gene isolated from sporulating bacteria isolated from fecal samples from privately owned dogs and dogs from the UZH animal facility. The sequences were compared with the reference sequence obtained from the undomesticated B. subtilis NCIB 3610 strain. Alignment gaps and missing data were eliminated in pairwise sequence comparisons. Bar, 0.0030 change per nucleotide position. (C) Top view of colonies of bacterial clones isolated from the feces of dogs from the UZH animal facility. Bacteria were grown on MSgg solid medium for 72 h at 30°C. The clone numbers assigned to the bacteria are denoted at the upper left corner of each panel. Bar, 1 cm.