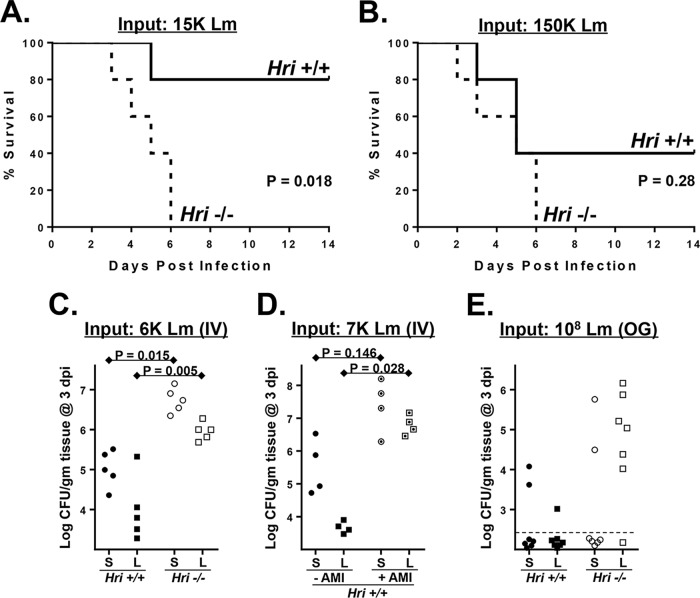
FIG 1.
HRI is protective against listeriosis. (A and B) Hri+/+ and Hri−/− mice (5 per group) were infected intravenously with 15,000 (A) or 150,000 (B) CFU of L. monocytogenes and monitored for 14 days. (P values were determined by a Mantel-Cox log rank test of a single representative experiment performed two times with similar results). (C) Hri+/+ mice (closed symbols) and Hri−/− mice (open symbols) were infected intravenously (IV) with L. monocytogenes and were humanely euthanized at 3 days postinfection (dpi). Data represent CFU in spleen (S; circles) and liver (L; squares) homogenates. (D) Hri+/+ mice were infected with L. monocytogenes and treated with either vehicle (closed symbols) or HRI AMI (dotted open symbols) on days 0, 1, and 2 postinfection. The load of L. monocytogenes in the spleen and liver was determined at 3 dpi. (E) Mice were inoculated orogastrically (OG) with the indicated dose of L. monocytogenes, and the bacterial loads in the spleen and liver were determined at 3 dpi by CFU assay. The dotted lines indicate detection limits. (P values were calculated using a Student t test of results of a single representative experiment performed two times.)