FIG 1.
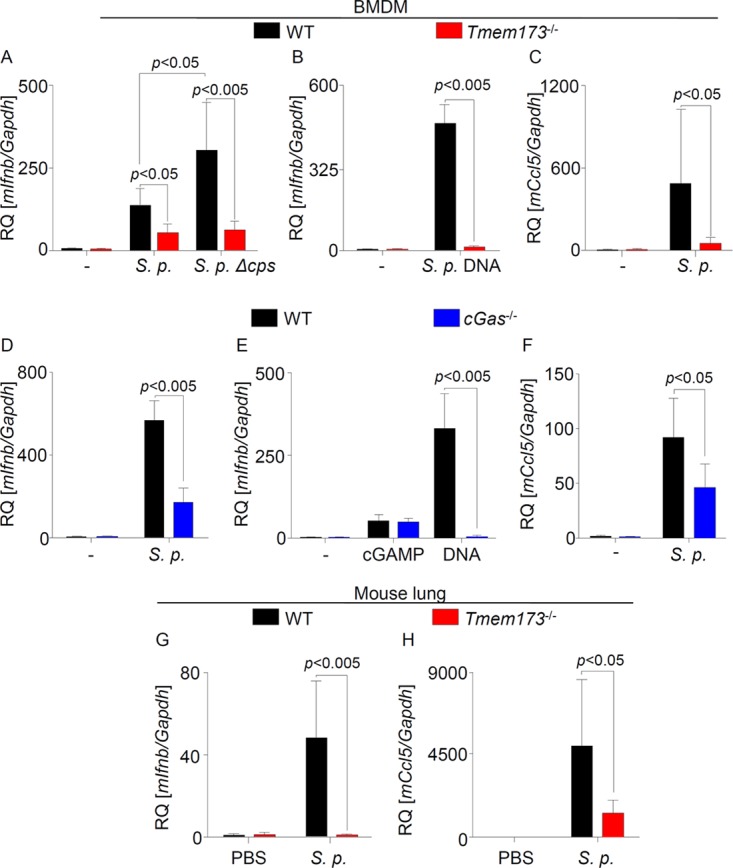
cGAS and STING mediate type I IFN responses to S. pneumoniae infection. (A and B) WT and Tmem173−/− mouse BMDMs were left untreated, were infected with S. pneumoniae (S. p.) or its Δcps isogenic mutant strain, or were stimulated with pneumococcal DNA for 6 h. Expression of Ifnb was quantified by qRT-PCR. (C) WT and Tmem173−/− BMDMs were left untreated or were infected with S. pneumoniae, and expression of Ccl5 was quantified by qRT-PCR. (D to F) BMDMs from cGas−/− mice were infected with S. pneumoniae or stimulated with synthetic DNA or cGAMP, and expression of Ifnb (D and E) and Ccl5 (F) was quantified by qRT-PCR. (G and H) WT and Tmem173−/− mice were intranasally infected with S. pneumoniae, and the expression of Ifnb and Ccl5 in the lungs was measured 48 h postinfection by qRT-PCR. Data from in vitro analyses are shown as means ± standard deviations (SD) from three independent experiments, measured in technical duplicates. Mouse data represent analyses of 7 mice. Statistical analyses were performed with the Mann-Whitney U test. Comparisons with a P value of <0.05 were considered significant. RQ, relative quantification.
