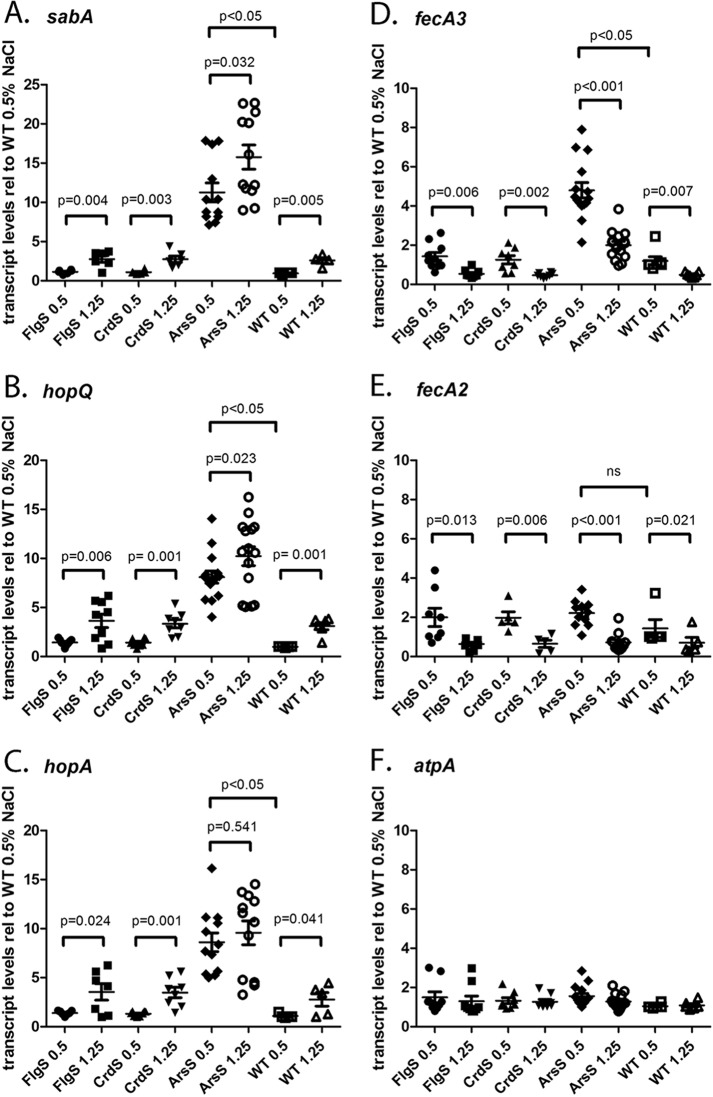
FIG 6.
ArsS regulates sabA, hopQ, hopA, and fecA3 expression. Strains containing insertional mutations in genes encoding ArsS, CrdS, or FlgS sensor kinases were cultured in BB-FBS-0.5% or BB-FBS-1.25% medium for 6 h. Transcript abundance was calculated using the ΔΔCT method, with each transcript signal normalized to the abundance of the gyrB internal control. The normalized transcript signals obtained for each sensor kinase mutant grown in BB-FBS-0.5% and BB-FBS-1.25% media were then compared to the normalized transcript signals obtained for wild-type H. pylori 7.13 grown in BB-FBS-0.5% medium (relative levels reported on the y axis). Each panel depicts the transcript levels for each strain and growth condition relative to that of the wild-type strain grown in BB-FBS-0.5% medium. The expression levels of the indicated genes (sabA, hopQ, hopA, fecA3, fecA2, and atpA) are shown. Each panel depicts results from at least seven independent biological sets of H. pylori strains grown in BB-FBS-0.5% and BB-FBS-1.25% media. Symbols indicate relative transcript abundance in the indicated H. pylori strains, grown under high-salt or routine conditions. The mean and standard error of the mean are reported. Statistical differences and corresponding P values are shown for comparisons of each strain grown under high-salt conditions and routine conditions (Student's t test). In addition, analyses of variance (ANOVA), followed by Dunn's multiple-comparison test, were conducted to examine statistical differences in the transcript levels expressed by mutant strains grown in BB-FBS-0.5% medium and the levels expressed by the WT strain grown in BB-FBS-0.5% medium.