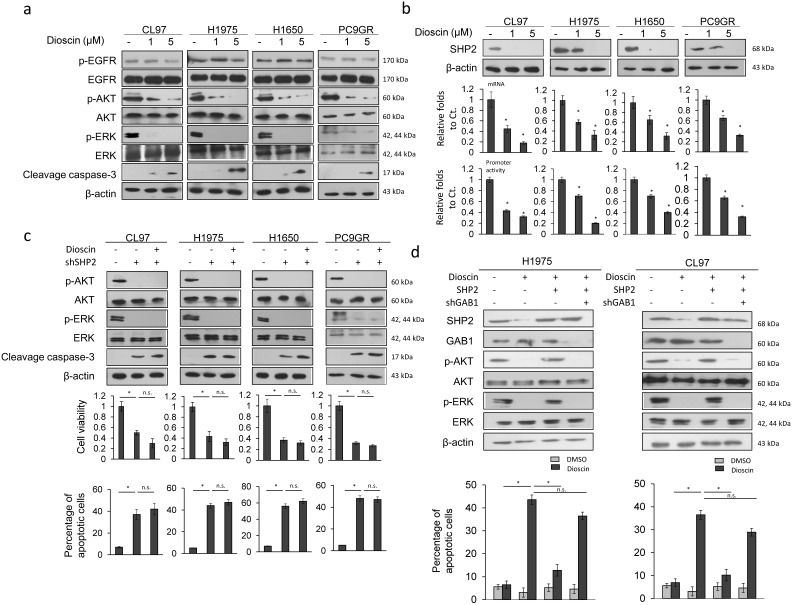
Figure 2.
Dioscin overcomes TKI resistance via simultaneous inhibition of the MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways due to decreased SHP2 expression and its interaction with GAB1. (a) The effect of dioscin on AKT and ERK signaling. Five hours after dioscin (-5 μM) treatment, the cell lysates were harvested and analyzed for signaling alteration by weocistern blotting with the indicated antibodies. (b) The effect of dioscin on SHP2 transcriptional level. Five hours after dosing cells with dioscin (0-5 μM), the cell lysates were prepared and analyzed for mRNA and promoter activity by real-time PCR and luciferase assays. The relative luciferase activity and mRNA expression was shown as fold-activation relative to the cells with vehicle treatment. (c) The effect of SHP2 knockdown on changes in cell viability and apoptosis induced by dioscin treatment. H1975, CL97, H1650, and PC9GR cells transfected with SHP2 shRNA were treated with 5 μM dioscin for 48 h. The cell viability was measured by MTT assays. Cell apoptosis was measured by annexinV-PI staining assays and flow cytometry. (d) The effect of SHP2 overexpression or/and GAB1 knockdown on the apoptosis induced by dioscin treatment. H1975 and CL97 cells transfected with SHP2 overexpression plasmid or/and GAB1 shRNA were treated with 5 μM dioscin for 48 h. Cell apoptosis was measured by annexinV-PI staining assays and flow cytometry. All data were collected from three independent experiments. The mean value and standard deviation are indicated as the column with error bars. The significant differences (*P < 0.05) in experimental groups were compared to indicated groups. N.s., Non-significance.