FIG 4 .
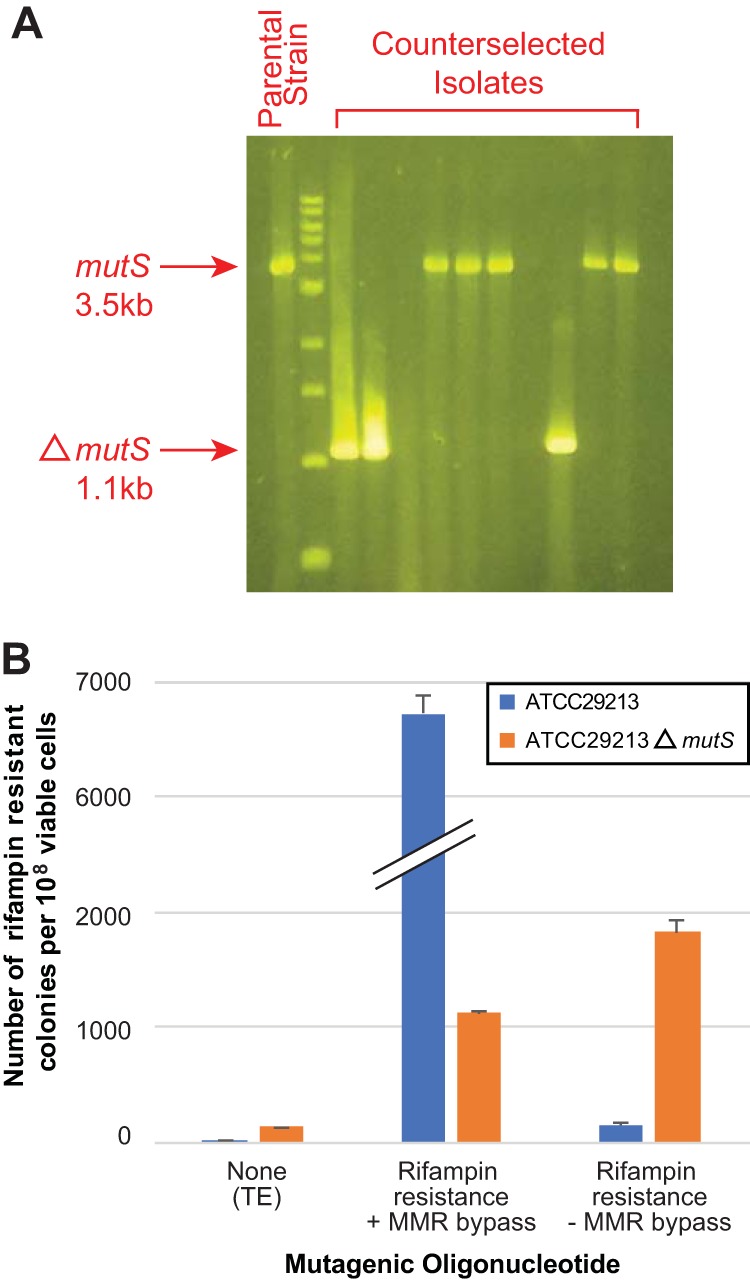
Recombineering of a 2.4-kb mutS deletion strain and effects of mutS deletion on subsequent recombineering. (A) PCR amplification of the mutS locus from representative colonies surviving counterselection. The wild-type allele corresponds to an amplicon 3.5 kb in size, whereas the engineered deletion results in a product at 1.1 kb. A 1-kb ladder is shown. (B) Recombineering efficiencies of the mutS deletion strain and mutS-intact parental strain compared to paired, mock-transformation controls lacking mutagenic oligonucleotide. Recombineering oligonucleotides encode rifampin resistance and either incorporate or lack silent mutations promoting bypass of MMR pathway repair. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means.
