Figure 2. The rate of protein degradation is decreased in S63del L and P0 OE sciatic nerves.
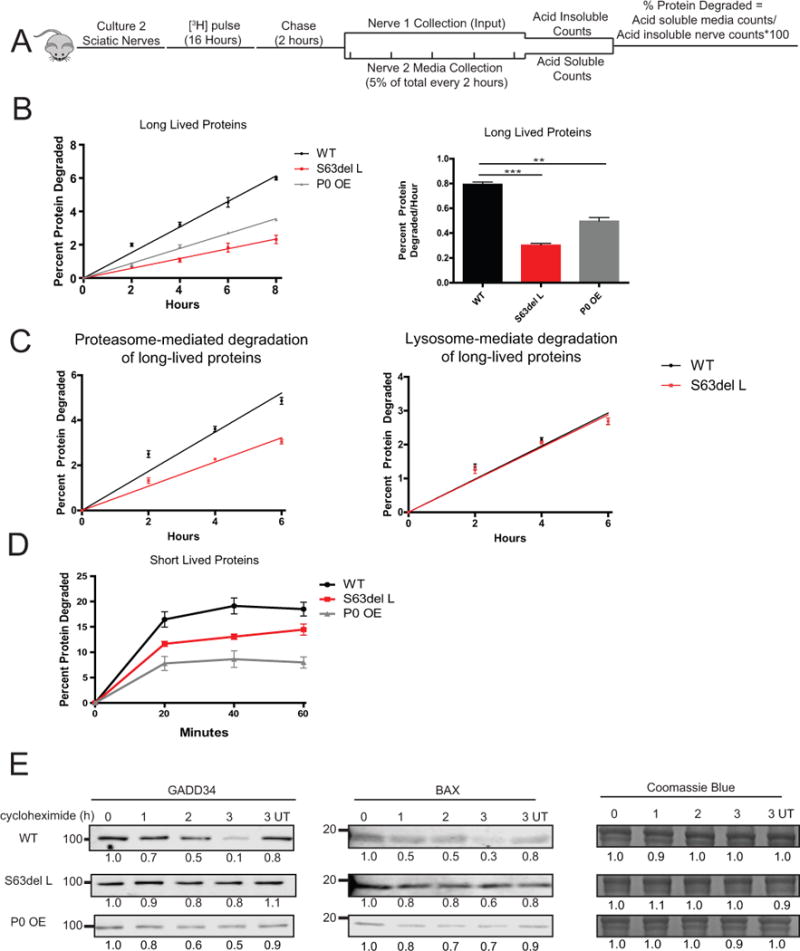
(A) To measure the rates of degradation of long-lived proteins, two sciatic nerve segments per mouse were pulse labeled ex vivo for 16 hours with 5 μM [3H]tyrosine, chased for 2 hours in media containing 2 mM nonradioactive tyrosine, and then acid-soluble counts per minute (CPM) in the media were determined. One nerve segment per mouse was lysed after the chase period and the [3H]tyrosine incorporation into protein was determined (input). Fresh chase media was added to the second nerve and 5% of the total media volume was removed every two hours, and the TCA soluble [3H]tyrosine in the media was determined. The percent protein degraded was calculated by dividing the TCA soluble radioactivity (degraded proteins) in the media at each time point by the TCA insoluble radioactivity in the nerve (radiolabeled proteins) at the end of the initial 2 hour chase period.
(B) S63del L and P0 OE sciatic nerves showed a reduction in the rate of degradation of long-lived proteins. The rate of proteolysis was calculated from the linear slopes. The mean rate of proteolysis for three individual mice per genotype was analyzed.
(C) The rate of proteasome-mediated degradation of long-lived proteins was decreased in S63del L sciatic nerves. The TCA soluble radioactivity in the media was plotted as a percentage of the total radioactivity incorporated into protein in the nerve. Proteasome-mediated degradation was determined in the presence of chloroquine and lysosome-mediated degradation was determined in the presence of bortezomib. N=3 mice per genotype, per condition.
(D) The degradation rate of short-lived proteins was reduced in S63del L and P0 OE. n=3 mice per genotype.
(E) The degradation of GADD34 and BAX, two well-described UPS substrate proteins, is decreased in S63del L and P0 OE sciatic nerves. Sciatic nerves were treated ex vivo with cycloheximide to block protein synthesis and collected at 1, 2 and 3 hours post cycloheximide addition. The levels of GADD34 and BAX remaining at each time point were measured by quantitative western analysis. The numbers below the blots correspond to the relative signal normalized to time 0. Coomassie blue staining (CBB) was used to estimate the total protein per lane.
