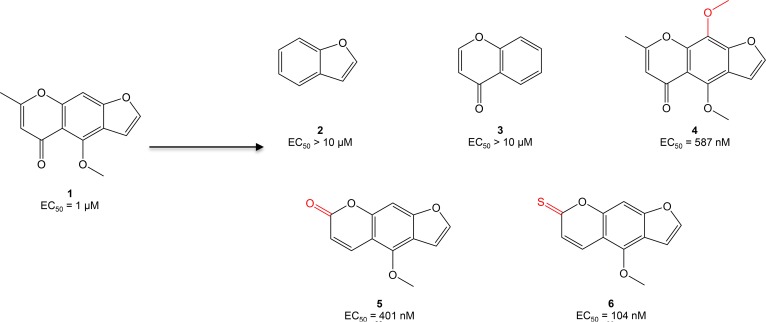
Figure 1. Optimization of compound 1 (C1, visnagin) in an in vivo model of DOX-induced cardiac toxicity.
EC50 values were calculated based on the percent of zebrafish rescued from the DOX cardiomyopathy phenotype (decreased cardiac contraction, pericardial edema, and decreased tail blood flow) as assessed under light microscopy at 40 hours after treatment. Initial SAR experiments included modification of the tricyclic structure of C1, addition of a methoxy group to the middle phenyl ring, and modification of substituents on the pyrone ring.