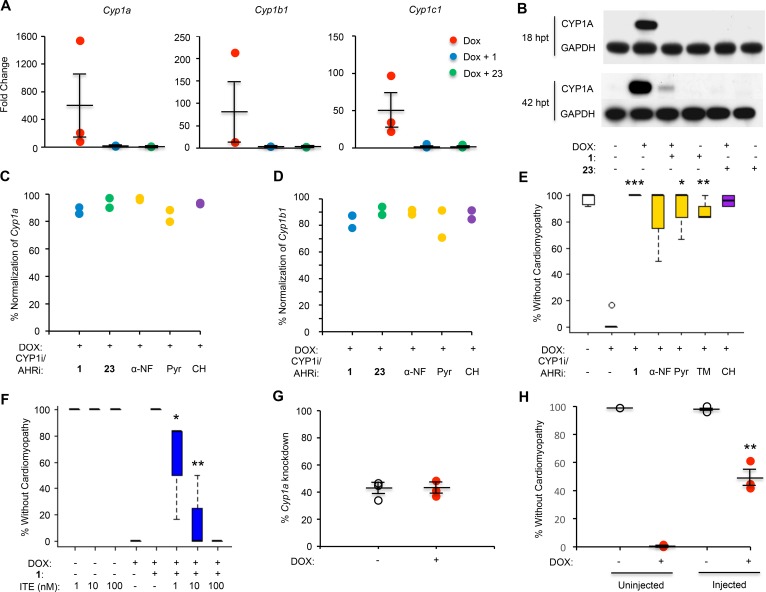
Figure 5. C1 and C23 inhibit induction of CYP1 enzymes by DOX.
(A) RNA levels of Cyp1a, Cyp1b1, and Cyp1c1 were increased in zebrafish treated with DOX. This effect was attenuated in zebrafish cotreated with C1 (10 μM) and C23 (10 μM), as measured by qPCR 18 hours after treatment (prior to the development of the cardiomyopathy phenotype). Expression levels were normalized to a housekeeping gene (β-actin or ornithine decarboxylase 1) and to control fish treated with DMSO. Data are depicted as mean ± SEM. (B) Western blotting of fish tissue lysate using a zebrafish-specific CYP1A antibody demonstrated induction of CYP1A by DOX and normalization by C1 (10 μM) and C23 (10 μM). RNA levels of Cyp1a (C) and Cyp1b1 (D) were normalized in zebrafish cotreated with DOX and either C1, C23, CYP1 inhibitors (CYP1i; α-NF and Pyr), or an AHR inhibitor (AHRi; CH) when compared with zebrafish treated with DOX alone. All cotreatments were administered at a concentration of 10 μM. α-NF, α-naphthoflavone; Pyr, pyrene; TM, 2,4,3’,5’-tetramethoxystilbene; CH, CH-233191. (E) Zebrafish cotreated with inhibitors of CYP1 and the AHR demonstrated increased percent rescue from the DOX cardiomyopathy phenotype (decreased cardiac contraction, pericardial edema, and decreased tail blood flow) as assessed under light microscopy at 40 hours after treatment. All inhibitors were administered at a dose of 10 μM. Student’s t test was performed, followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple hypotheses. (F) Percent rescue from the DOX cardiomyopathy phenotype in zebrafish cotreated with C1 (20 μM) and the AHR agonist methyl 2-(1H-indole-3-carbonyl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylate (ITE). One-way ANOVA was performed, followed by the Tukey’s test. (G) Using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis, single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) targeting Cyp1a were injected into zebrafish embryos to generate potential founder (F0) Cyp1-KO fish. Across this mosaic population, injected zebrafish demonstrated 40% knockdown of Cyp1a RNA levels as assessed by qPCR compared with uninjected zebrafish from the same clutch. (H) Zebrafish injected with sgRNAs targeting Cyp1a demonstrated nearly 50% rescue from DOX-induced cardiomyopathy. Data represent mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA was performed, followed by the Tukey’s test. For all chemical treatments in zebrafish, data represent 12 fish treated per condition per experiment, and each experiment was repeated 3 times. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001.